









Tissues in Biology: Types, Functions, and Structure
Discover the various types of tissues in biology, including epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissues. Learn about their functions, structures, and real-life applications through detailed explanations and informative diagrams.Tissues are groups of similar cells that work together to perform specific functions within an organism. They form the structural and functional foundation of organs, enabling protection, support, movement, and signal transmission. Understanding tissues is essential for studying the complexities of biological systems and their roles in maintaining health.

Sweta | July 17, 2024
Share this Page on:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
- 1. Introduction to Tissues
- 2. What are Tissues
- 3. How to Identify Different Types of Tissues
- 4. Rules for Classifying Tissues
- 5. Types of Tissues
- 6. Properties of Tissues
- 7. Tissues Solved Examples
- 8. Practice Questions on Tissues
- 9. FAQs on Tissues
- 10. Real-life application of Tissues
- 11. Conclusion
1. Introduction to Tissues:
Tissues are cells that work together to perform a specific function in an organism. In biology, understanding tissues is crucial because they form the structural and functional foundation of organs and the body as a whole. Let's delve into the world of tissues and explore their various types and functions.
2. What are Tissues:
Tissues are collections of similar cells that collaborate to perform specialized activities. They are the building blocks of organs and play a vital role in maintaining the health and function of an organism. There are four primary types of tissues in animals: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissues. Each type has distinct characteristics and functions.
3. How to Identify Different Types of Tissues:
Identifying different types of tissues involves examining their structure and function. Here’s a brief overview of each type:
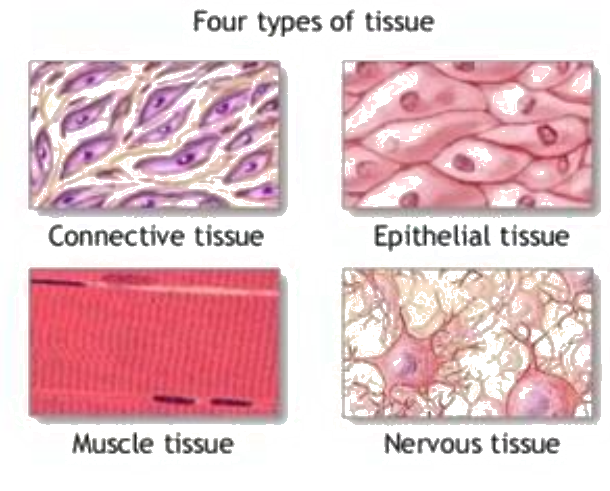
- Epithelial Tissue: Covers body surfaces and lines body cavities. It acts as a barrier and is involved in absorption, secretion, and protection.
- Connective Tissue: Supports, binds, and protects other tissues and organs. It includes bone, cartilage, fat, and blood.
- Muscle Tissue: Responsible for movement. It includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle tissues.
- Nervous Tissue: Comprises neurons and supporting cells, essential for transmitting signals and coordinating bodily functions.
4. Rules for Classifying Tissues:
To classify tissues, biologists look at several factors, including the shape and arrangement of cells, the presence of extracellular matrix, and the specific functions of the tissue. Understanding these criteria helps in accurately identifying and categorizing tissues.
5. Types of Tissues:
(i) Epithelial Tissue
Definition: Epithelial tissue is a cell sheet covering body surfaces or lines body cavities. Its primary functions include protection, secretion, absorption, and filtration. Epithelial tissues are classified based on the shape of the cells and the number of cell layers.
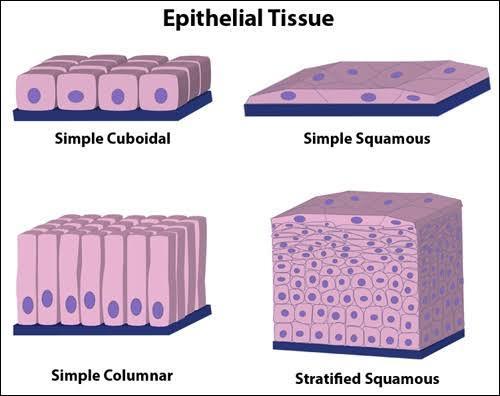
Structure & Function: Epithelial tissues can be simple (a single layer of cells) or stratified (multiple layers of cells). The cell shapes can be squamous (flat), cuboidal (cube-shaped), or columnar (tall and column-like). Each type is adapted to specific functions, such as diffusion, filtration, or secretion.
(ii) Connective Tissue
Definition: Connective tissue is the body's most diverse and abundant tissue type. It provides support, binds together, and protects tissues and organs. Connective tissues are characterized by an extracellular matrix that contains fibers and ground substances.
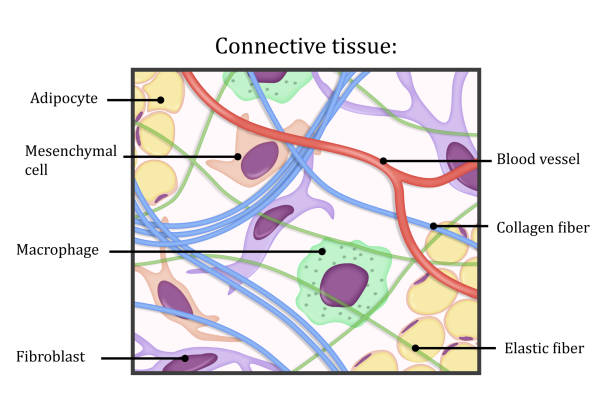
Types & Function: Connective tissues include loose connective tissue (e.g., adipose tissue), dense connective tissue (e.g., tendons), cartilage, bone, and blood. Each type has specific roles, such as providing structural support, transporting nutrients, and storing energy.
(iii) Muscle Tissue
Definition: Muscle tissue is specialized for contraction and movement. It is composed of cells that can shorten and generate force. There are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth.
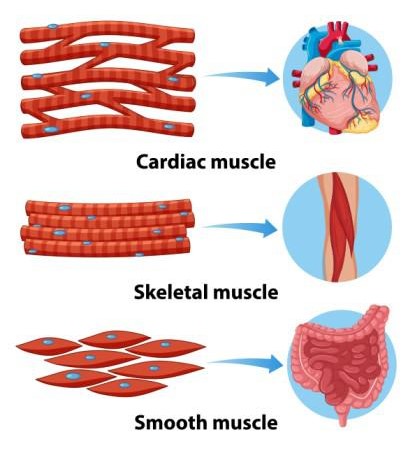
Types & Function:
- Skeletal Muscle: Voluntary muscles attached to bones, responsible for body movements.
- Cardiac Muscle: Involuntary muscle found in the heart that pumps blood.
- Smooth Muscle: Involuntary muscle found in walls of internal organs, responsible for movements like peristalsis.
(iv) Nervous Tissue
Definition: Nervous tissue transmits electrical signals throughout the body. It consists of neurons, which transmit impulses, and glial cells, which provide support and protection.
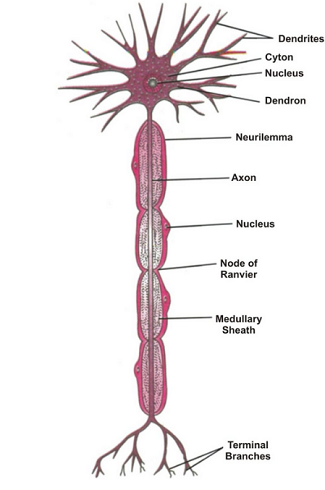
Structure & Function: Neurons have a cell body, dendrites, and axons. They transmit signals to and from the brain and spinal cord. Glial cells support neurons and maintain the environment around them.
6. Properties of Tissues:
- Epithelial Tissue: High cellularity, polarity, avascular but innervated, and regenerative capacity.
- Connective Tissue: Diverse, with abundant extracellular matrix and varying degrees of vascularity.
- Muscle Tissue: Contractility, excitability, extensibility, and elasticity.
- Nervous Tissue: Excitability and conductivity, with specialized cells for rapid communication.
7. Tissues Solved Examples:
Example 1: Identifying Epithelial Tissue
Solution: Consider a sample with a single layer of flat cells. This is likely a simple squamous epithelium adapted for diffusion and filtration.
Example 2: Identifying Connective Tissue
Solution: A sample with a gel-like matrix and embedded fibers is likely a type of connective tissue, such as cartilage or loose connective tissue.
8. Practice questions on Tissues:
Question 1: Identify the type of epithelial tissue in the stomach lining.
Question 2: Describe the characteristics of dense connective tissue.
Question 3: Explain the differences between the three types of muscle tissue.
Question 4: Discuss the role of glial cells in nervous tissue.
9. FAQs on Tissues:
What is epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue is a cell sheet covering body surfaces or lines of body cavities, performing functions like protection, secretion, and absorption.
What is connective tissue?
Connective tissue supports binds and protects other tissues and organs, including bone, cartilage, and blood types.
What are the main types of muscle tissue?
The main types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth, each with unique functions and characteristics.
What is the function of nervous tissue?
Nervous tissue transmits electrical signals throughout the body, coordinating bodily functions and responses to stimuli.
How do tissues differ from organs?
Tissues are groups of similar cells that perform a specific function, while organs are structures composed of multiple tissue types working together for a common purpose.
10. Real-life application of Tissues:
Understanding tissues is fundamental in medicine and biology. For instance, knowing the properties of epithelial tissue helps diagnose and treat skin diseases, while understanding muscle tissue is crucial for addressing muscular disorders. Research on nervous tissue aids in the development of treatments for neurological conditions.
11. Conclusion:
Tissues are the building blocks of the body's organs and systems, each with unique structures and functions essential for life. By studying tissues, we gain insight into the complex workings of the human body, leading to advances in medicine and healthcare. Whether it’s epithelial tissue protecting our skin or nervous tissue transmitting signals, each type plays a crucial role in maintaining health and functionality.
If you have any suggestions regarding the improvement of the content of this page, please write to me at My Official Email Address: [email protected]
Are you Stuck on homework, assignments, projects, quizzes, labs, midterms, or exams?
To get connected to our tutors in real-time. Sign up and get registered with us.
Blog Information
Blog Author: Sweta
Blog Publisher: Doubtlet
Comments(0)
Your comment will be reviewed before it is published.
Leave a comment