









Discriminant Calculator
This calculator will help you to find the Discriminant of a Quadratic Equation with the steps shown.Related Calculator:Quadratic Equation Calculator
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...

Neetesh Kumar | January 16, 2025
Share this Page on:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
- 1. Introduction to the Discriminant Calculator
- 2. What is the Formulae used
- 3. How do I find the Discriminant?
- 4. Why choose our Discriminant Calculator?
- 5. A Video for explaining this concept
- 6. How to use this calculator?
- 7. Solved Examples on Discriminant
- 8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 9. What are the real-life applications?
- 10. Conclusion
The Discriminant Calculator is a valuable tool for analyzing quadratic equations and understanding the nature of their roots. Whether you’re solving equations for academic purposes or practical applications, this calculator makes it quick and easy to compute the discriminant and determine the type of solutions.
1. Introduction to the Discriminant Calculator
In quadratic equations of the form , the discriminant plays a crucial role in determining the nature of the roots. By evaluating a single expression, you can determine whether the equation has real, imaginary, unique, or repeated roots.
Our Discriminant Calculator for a Table is designed for efficiency, allowing you to input multiple equations simultaneously. From students and teachers to researchers and engineers, this tool is indispensable for solving quadratic equations.
2. What is the Formulae used?
The discriminant of a quadratic equation is given by:
Where:
- : Discriminant
- : Coefficient of
- : Coefficient of
- : Constant term
Understanding the Nature of Roots:
- : Two distinct real roots.
- : One repeated real root.
- : Two complex (imaginary) roots.
This formula helps determine the characteristics of the quadratic equation without solving it entirely.
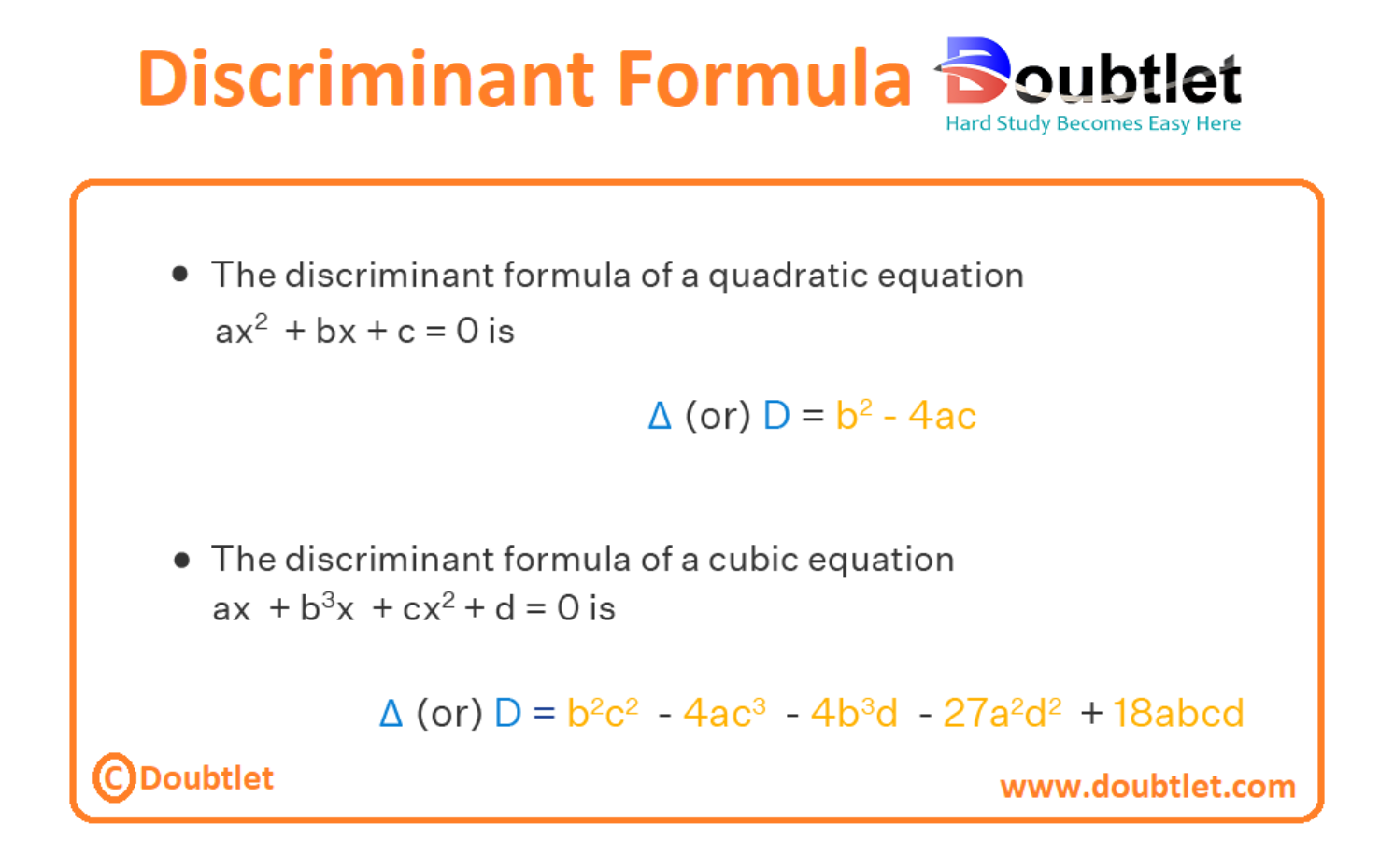
What is the Discriminant of a Quadratic Equation?
The discriminant is the part of the quadratic formula found within the square root. For a quadratic of the form , its discriminant is . A quadratic equation has , or solutions depending if the value of the discriminant is positive, zero or negative respectively.
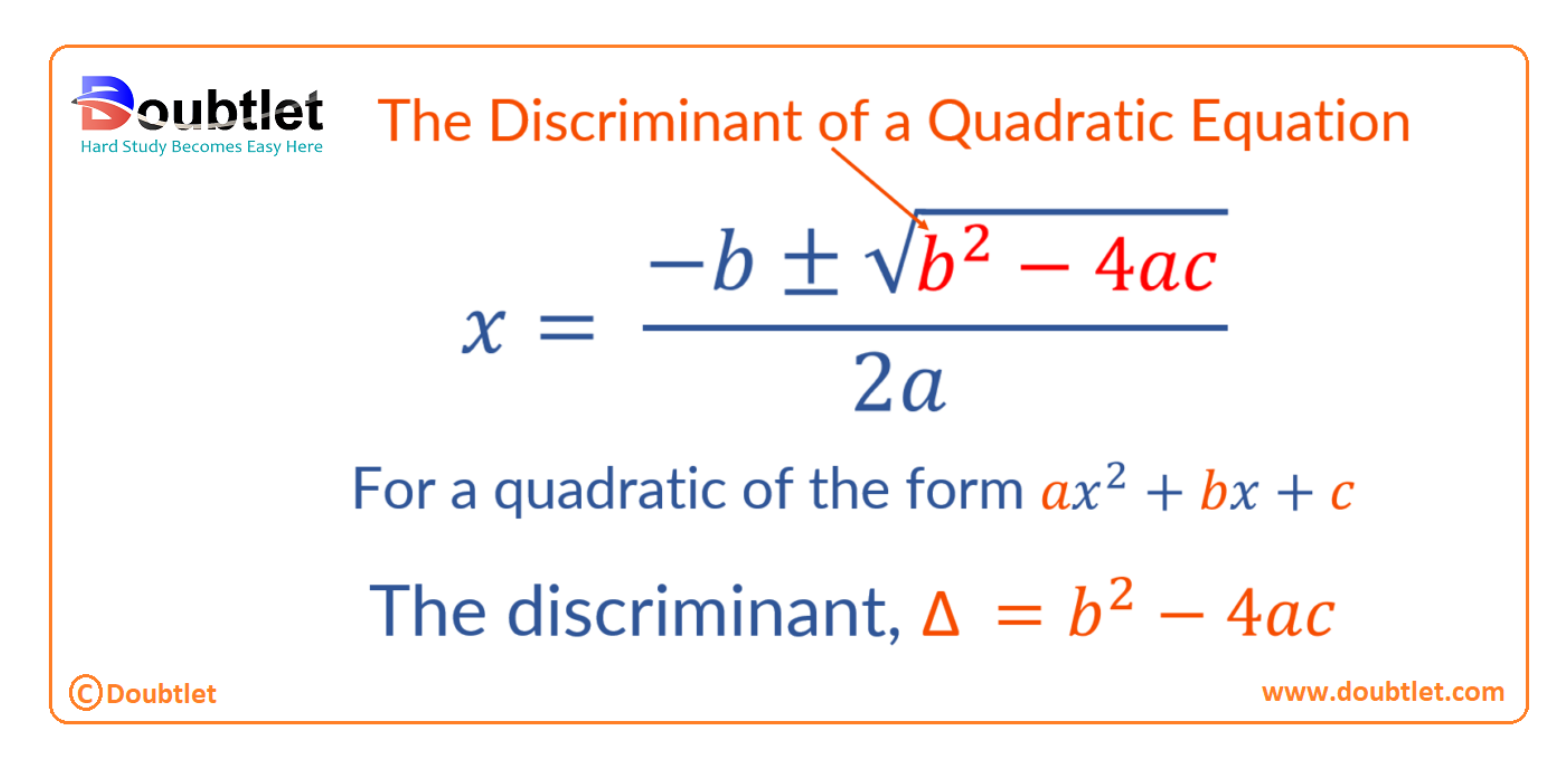
The discriminant, , is represented by the delta symbol, .
The discriminant formula is:
where:
- is the coefficient of ,
- is the coefficient of , and
- is the constant term of a quadratic equation.
Example:
Calculate the discriminant of .
Step 1: Identify the coefficients.
- The coefficient of is . Therefore, .
- The coefficient of is . Therefore, .
- The constant term is . Therefore, .
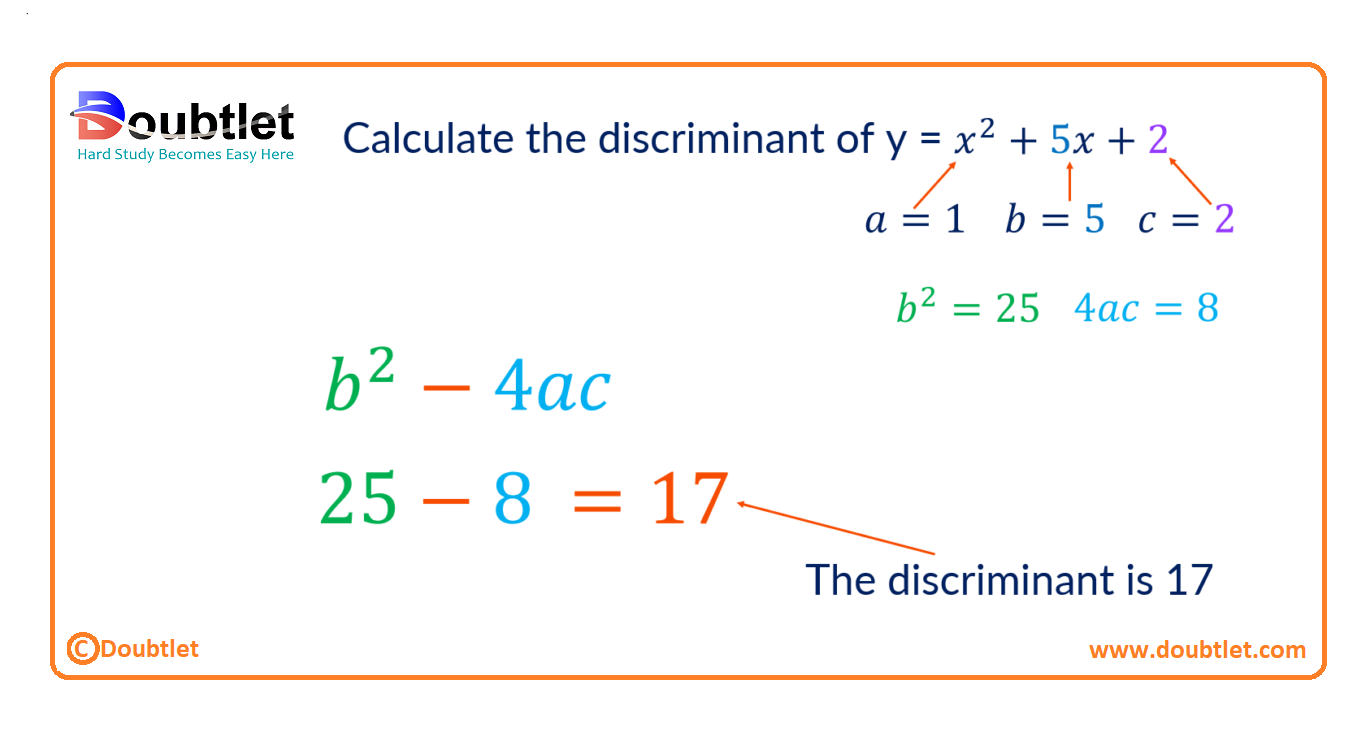
We substitute the values of , , and into the formula for the discriminant, .
and
Thus:
The discriminant is .
Importance of the Discriminant
The discriminant provides information about the number and type of solutions of a quadratic equation:
- Positive discriminant : There are distinct real solutions.
- Zero discriminant : There is repeated real solution.
- Negative discriminant : There are no real solutions, but complex solutions.
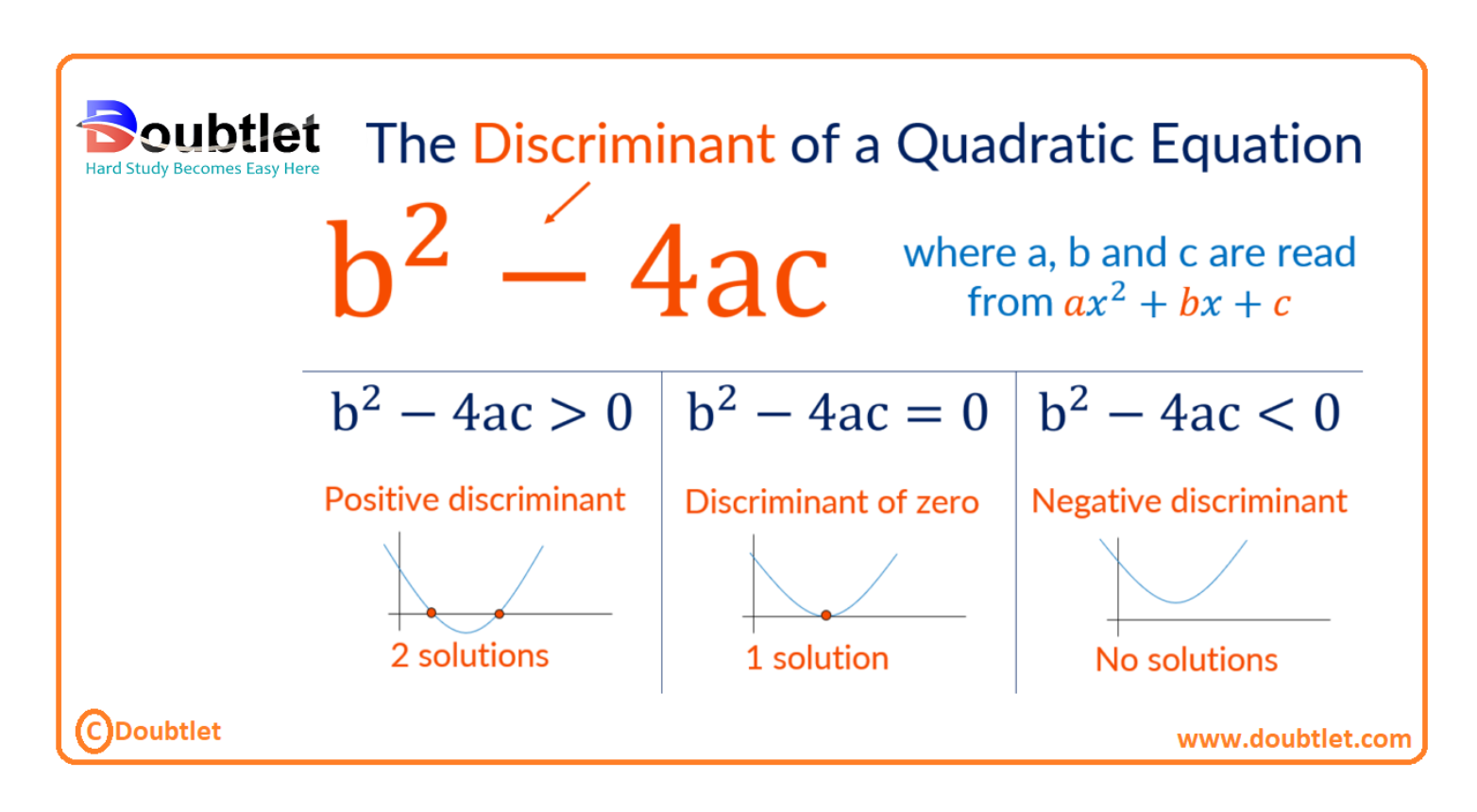
The number of solutions to a quadratic equation determines the number of roots of the equation. The roots correspond to the points where the quadratic graph intersects the -axis, known as the -axis intercepts.
The following table shows the number of roots for a positive, negative or zero discriminant.
| Value of the discriminant |
| Numbers of Roots |
| > 0 | Positive | Two |
| = 0 | Zero | One |
| < 0 | Negative | Zero |
3. How Do I Find the Discriminant?
To calculate the discriminant manually:
- Identify the Coefficients: Extract , , and from the equation.
- Substitute into the Formula: Compute .
- Interpret the Result: Use the value of to determine the type of roots.
Example:
For :
-
Coefficients:
- ,
- ,
- .
-
Discriminant:
-
Interpretation:
- , so the equation has two distinct real roots.
When dealing with multiple equations, our calculator automates this process for quick and accurate results.
How to Calculate the Discriminant
To calculate the discriminant of a quadratic equation, the formula is . Substitute the values of , , and after reading them from a quadratic equation of the form .
Example:
For :
- ,
- ,
- .
-
Calculate :
-
Calculate :
-
Discriminant:
The discriminant .
Key Points to Remember:
- is always positive. When we square a negative number, it results in a positive value.
- If is negative, we need to perform addition because subtracting a negative number is equivalent to adding.
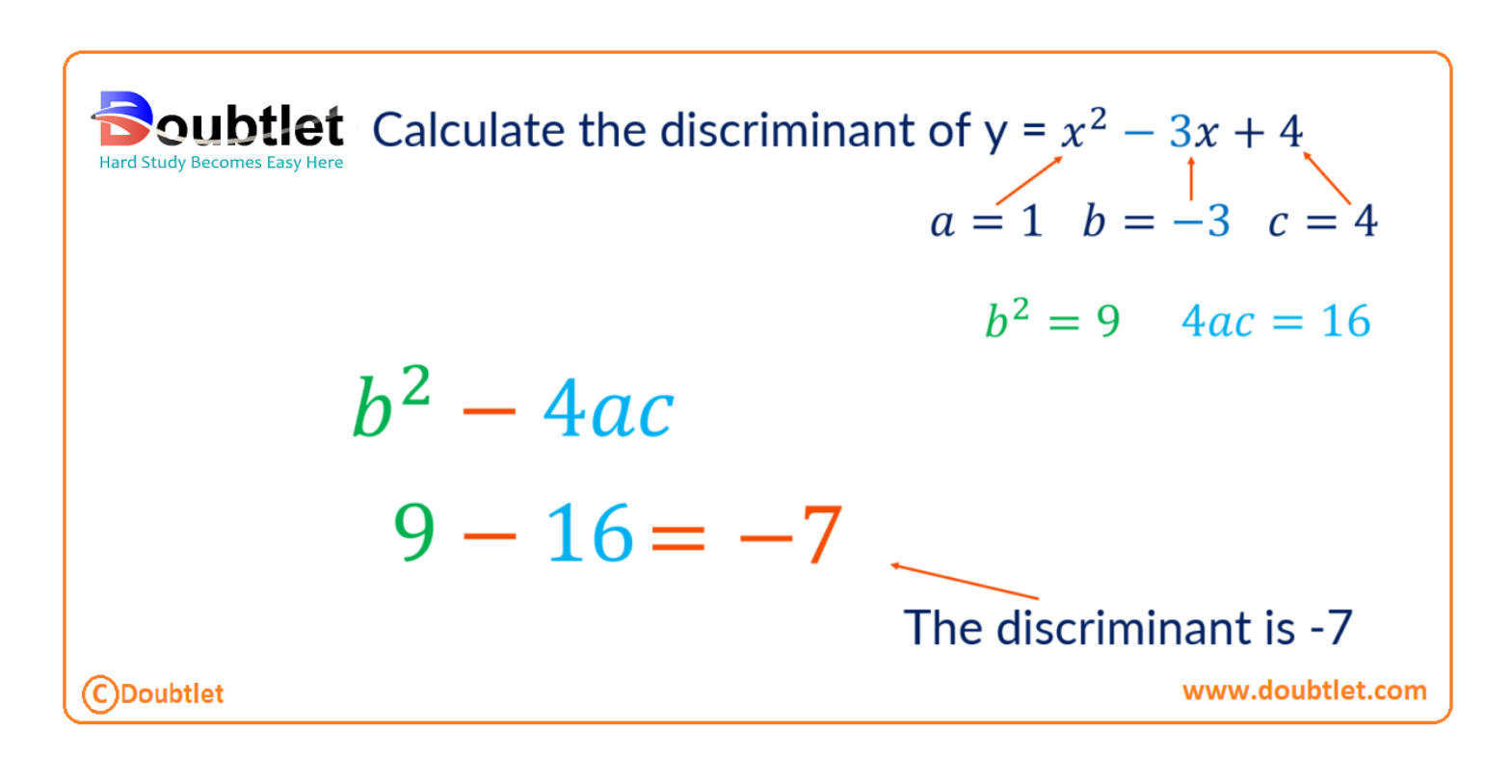
Understanding the Discriminant
The discriminant in a quadratic equation helps determine the nature of the roots of the equation.
For a quadratic equation in the form:
The discriminant is given by:
Discriminant and Nature of Roots
- If : The equation has two distinct real roots.
- If : The equation has one real root (a double root).
- If : The equation has two complex roots.
Solved Examples
Example 1:
Find the discriminant of and determine the nature of the roots.
Solution:
-
Identify coefficients: , , .
-
Compute the discriminant:
-
Interpretation:
- , so the equation has two distinct real roots.
Example 2:
Find the discriminant of and determine the nature of the roots.
Solution:
-
Identify coefficients: , , .
-
Compute the discriminant:
-
Interpretation:
- , so the equation has one real root (a double root).
Example 3:
Find the discriminant of and determine the nature of the roots.
Solution:
-
Identify coefficients: , , .
-
Compute the discriminant:
-
Interpretation:
- , so the equation has two complex roots.
Graph Explanation
Let’s plot graphs of quadratic equations for the above examples to visualize the effect of the discriminant on the nature of roots.
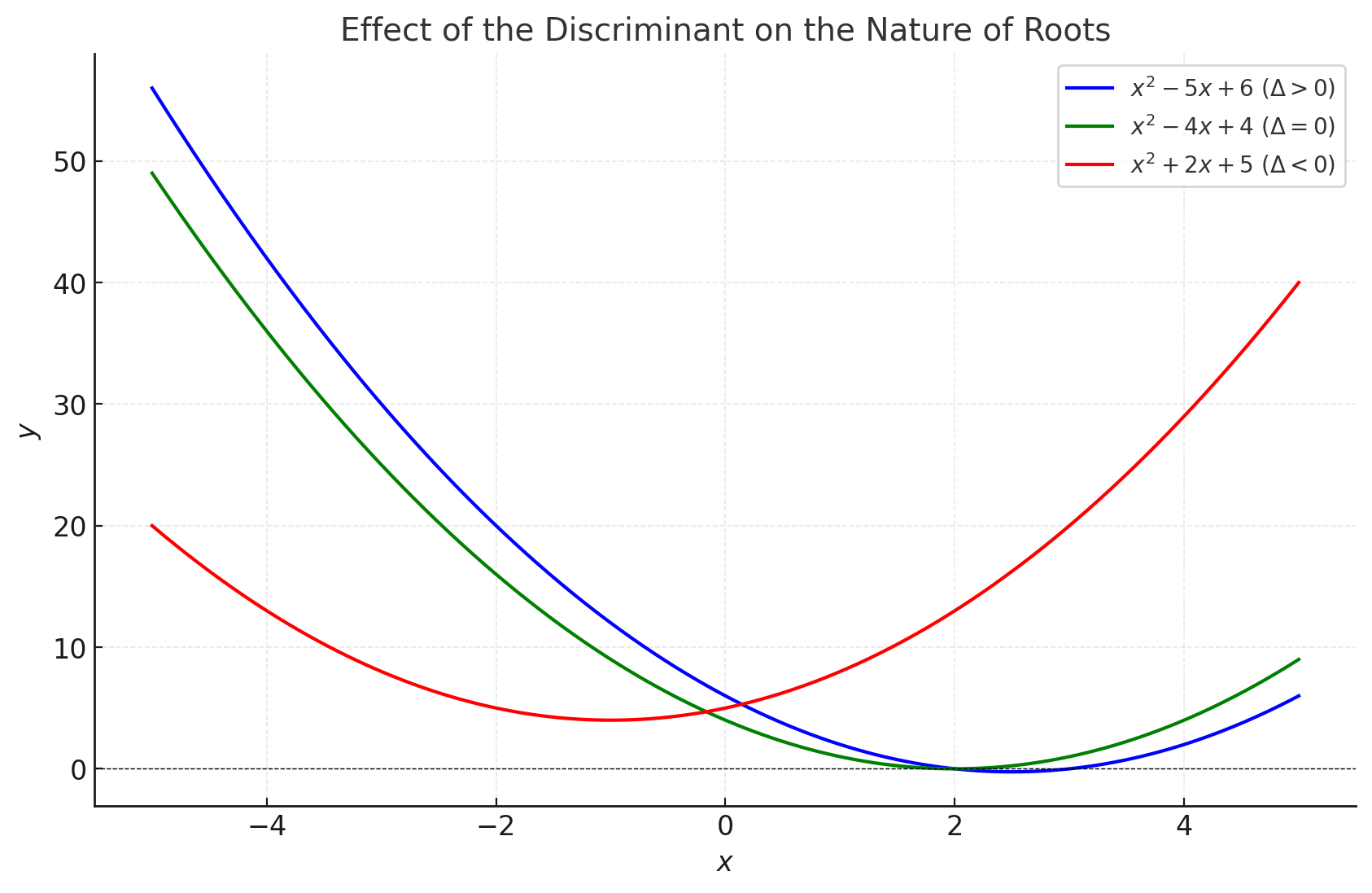
Explanation of the Graph:
-
Blue Curve :
- , so the equation has two distinct real roots.
- The curve intersects the -axis at two points.
-
Green Curve :
- , so the equation has one real root (a double root).
- The curve touches the x-axis at exactly one point.
-
Red Curve :
- , so the equation has two complex roots.
- The curve does not intersect the -axis.
Key Insights:
- The discriminant determines the interaction of the quadratic curve with the -axis.
- Positive discriminants produce two -intercepts.
- Zero discriminants produce one -intercept.
- Negative discriminants produce no -intercepts.
4. Why Choose Our Discriminant Calculator?
Our calculator page provides a user-friendly interface that makes it accessible to both students and professionals. You can quickly input your square matrix and obtain the matrix of minors within a fraction of a second.
Our calculator saves you valuable time and effort. You no longer need to manually calculate each cofactor, making complex matrix operations more efficient.
Our calculator ensures accurate results by performing calculations based on established mathematical formulas and algorithms. It eliminates the possibility of human error associated with manual calculations.
Our calculator can handle all input values like integers, fractions, or any real number.
Alongside this calculator, our website offers additional calculators related to Pre-algebra, Algebra, Precalculus, Calculus, Coordinate geometry, Linear algebra, Chemistry, Physics, and various algebraic operations. These calculators can further enhance your understanding and proficiency.
5. A video based on how to Evaluate the Discriminant.
6. How to use this calculator?
Using the Discriminant Calculator is straightforward:
- Input Coefficients: Enter the values of , , and for your equation(s).
- Click Calculate: Instantly view the discriminant and root nature.
- Analyze Results: Use the discriminant to determine the characteristics of the quadratic equation.
This tool ensures fast, accurate results, even for large datasets.
7. Solved Examples on Discriminant
Example 1:
Equation:
Steps:
-
Coefficients: , , .
-
Discriminant:
-
Result: , so the equation has one repeated real root.
Example 2: Tabular Data:
| Equation |
|
|
|
Discriminant |
Nature of Roots |
|
|
|
|
|
Calculate |
Calculate |
|
|
|
|
|
Calculate |
Calculate |
Steps:
-
Input each equation into the calculator.
-
Compute the discriminant and interpret results:
- : Two distinct real roots.
- : One repeated real root.
- : Two imaginary roots.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the discriminant?
The discriminant determines the nature of roots for a quadratic equation.
Q2. How do I interpret the discriminant?
- : Two distinct real roots.
- : One repeated real root.
- : Two complex roots.
Q3. Is this calculator free?
Yes, our Discriminant Calculator is completely free to use.
Q4. Can it handle large datasets?
Yes, it’s optimized for processing tabular data efficiently.
Q5. Does it work for non-quadratic equations?
No, the discriminant applies specifically to quadratic equations.
Q6. Is the calculator mobile-friendly?
Yes, it works seamlessly on all devices.
Q7. Does it show intermediate steps?
Yes, detailed calculations are displayed for better understanding.
Q8. Can I export the results?
Yes, you can download the results for further use.
9. What are the real-life applications?
The discriminant is widely used in:
- Engineering: Solve equations in structural analysis and mechanics.
- Finance: Model quadratic trends in financial forecasting.
- Education: Help students understand quadratic equations.
- Physics: Analyze motion and forces involving quadratic relationships.
- Computer Graphics: Handle parabolic curves and rendering algorithms.
Fictional Anecdote: Alex, an engineer, uses our Discriminant Calculator to analyze quadratic equations in a structural project. By quickly identifying equations with real roots, Alex improves project efficiency and reduces errors.
10. Conclusion
The Discriminant Calculator is a powerful tool for solving and analyzing quadratic equations. It simplifies complex calculations, ensures accuracy, and saves time, making it ideal for students, educators, and professionals alike.
Ready to streamline your quadratic analysis? Try our Discriminant Calculator today and experience the ease of accurate computations!
If you have any suggestions regarding the improvement of the content of this page, please write to me at My Official Email Address: doubt@doubtlet.com
Are you Stuck on homework, assignments, projects, quizzes, labs, midterms, or exams?
To get connected to our tutors in real time. Sign up and get registered with us.
Percent to Fraction calculator
Scientific Notation calculator
Hypergeometric Distribution Calculator
Normal Distribution Calculator
Laplace Transform Calculator
X and Y Intercepts Calculator
FOIL Method Calculator









