









Logarithm Calculator
This calculator will help you to evaluate logarithm value with the steps shown.Related Calculators:Exponential Function Calculator
Loading...

Neetesh Kumar | January 21, 2025
Share this Page on:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
- 1. Introduction to the Logarithm Calculator
- 2. What is the Formulae used
- 3. How Do I Find the Logarithm?
- 4. Why Choose Our Logarithm Calculator?
- 5. A Video for explaining this concept
- 6. How to use this calculator?
- 7. Solved Examples on Logarithm
- 8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 9. What are the real-life applications?
- 10. Conclusion
The Logarithm Calculator is a powerful tool designed to simplify logarithmic calculations. Whether you’re a student solving equations, a professional analyzing data, or simply curious about logarithmic concepts, this calculator makes it easy to compute results accurately and quickly. With support for multiple bases and tabular data, it’s the ideal solution for all your logarithmic needs.
1. Introduction to the Logarithm Calculator
A logarithm answers the question: "To what power must the base be raised to produce a given number?" It’s an essential concept in mathematics, used in fields like engineering, computer science, and finance.
Our Logarithm Calculator streamlines the process, allowing you to calculate logarithms for individual values or entire datasets in a table. With its intuitive interface and robust functionality, it caters to both beginners and professionals.
2. What is the Formulae used?
The general formula for a logarithm is:
Where:
- : Base of the logarithm (e.g., , , or any positive number).
- : The number whose logarithm is being calculated.
- : The exponent or result.
Common Logarithm:
For base :
Natural Logarithm:
For base ():
Log Formulas
Before learning log formulas, let us recall what are logs (logarithms). A logarithm is just another way of writing exponents. When we cannot solve a problem using the exponents, then we use logarithms. There are different logarithm formulas that are derived by using the laws of exponents. Let us learn them using a few solved examples.
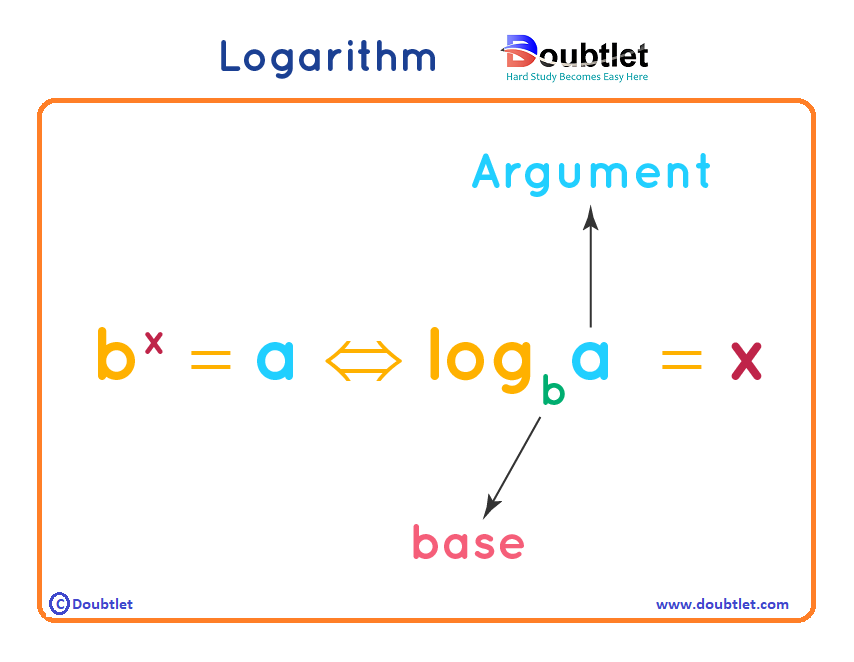
What are Log Formulas?
Before going to learn the log formulas, let us recall a few things. There are two types of logarithms, common logarithm (which is written as "log" and its base is if not mentioned) and natural logarithm (which is written as "ln" and its base is always ). The below logarithm formulas are shown for common logarithms. However, they are all applicable for natural logarithms as well. Here are the most commonly used log formulas.
Some of these rules have specific names like is called the product formula of logs. In the same way, all the properties along with their names are mentioned in the table below.
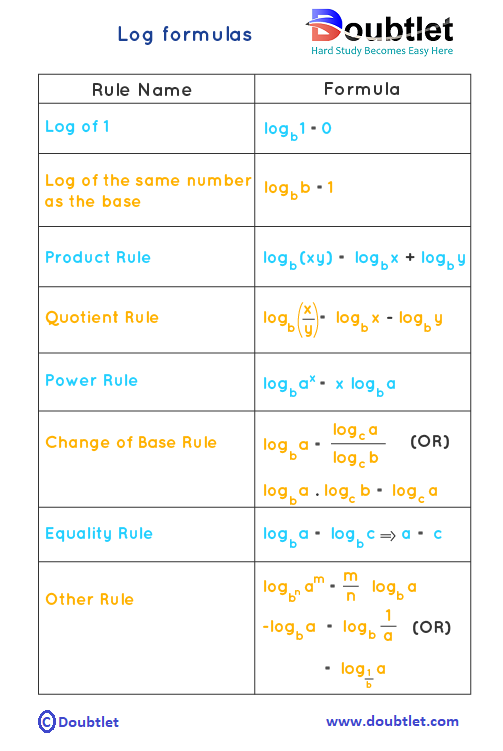
Logarithmic Formulas Derivation
Here is the derivation of some important log formulas. We use the laws of exponents in the derivation of log formulas.
Product Formula of Logarithms
The product formula of logs is, .
Derivation:
Let us assume that and . Then by the definition of logarithm,
and .
Then (by a law of exponents, ).
Converting into logarithmic form, we get
.
Substituting the values and here,
.
Quotient Formula of Logarithms
The quotient formula of logs is, .
Derivation:
Let us assume that and . Then by the definition of logarithm,
and .
Then (by a law of exponents, ).
Converting into logarithmic form, we get
.
Substituting the values and here,
.
Power Formula of Logarithms
The power formula of logarithms says .
Derivation:
Let . Then by the definition of logarithm, .
Raising both sides by , we get
.
(by a law of exponents, ).
Converting this back into logarithmic form,
.
Substitute here,
.
Change of Base Formula of Logarithms
The change of base formula of logs says .
Derivation:
Assume that , , and .
Converting these into exponential forms,
... (1)
... (2)
... (3)
From (1) and (2),
(from (3))
Since the bases are the same, the powers also should be the same.
(or) .
Substituting the values of , , and here back,
.
3. How Do I Find the Logarithm?
To calculate a logarithm manually:
- Identify the Base and Value: Determine the base () and the value ().
- Use the Definition: Solve for .
- Approximate if Necessary: For non-integer results, use a calculator or logarithmic tables.
Example (Base 10):
Find :
- , .
- Solve .
- , because .
Our Logarithm Calculator automates this process for any base and multiple values.
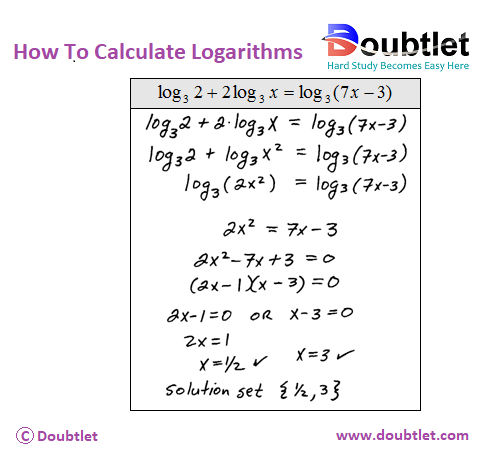
Understanding Logarithms
A logarithm is the inverse of an exponent. For a number , the logarithm to the base is defined as:
Where:
- and (base of the logarithm),
- (input value),
- is the output of the logarithm.
Example: Solve
Problem: Find the value of .
Solution:
-
By definition:
. -
Solve :
.
Answer:
Graph Explanation
Let’s visualize the logarithmic function , including the specific point .
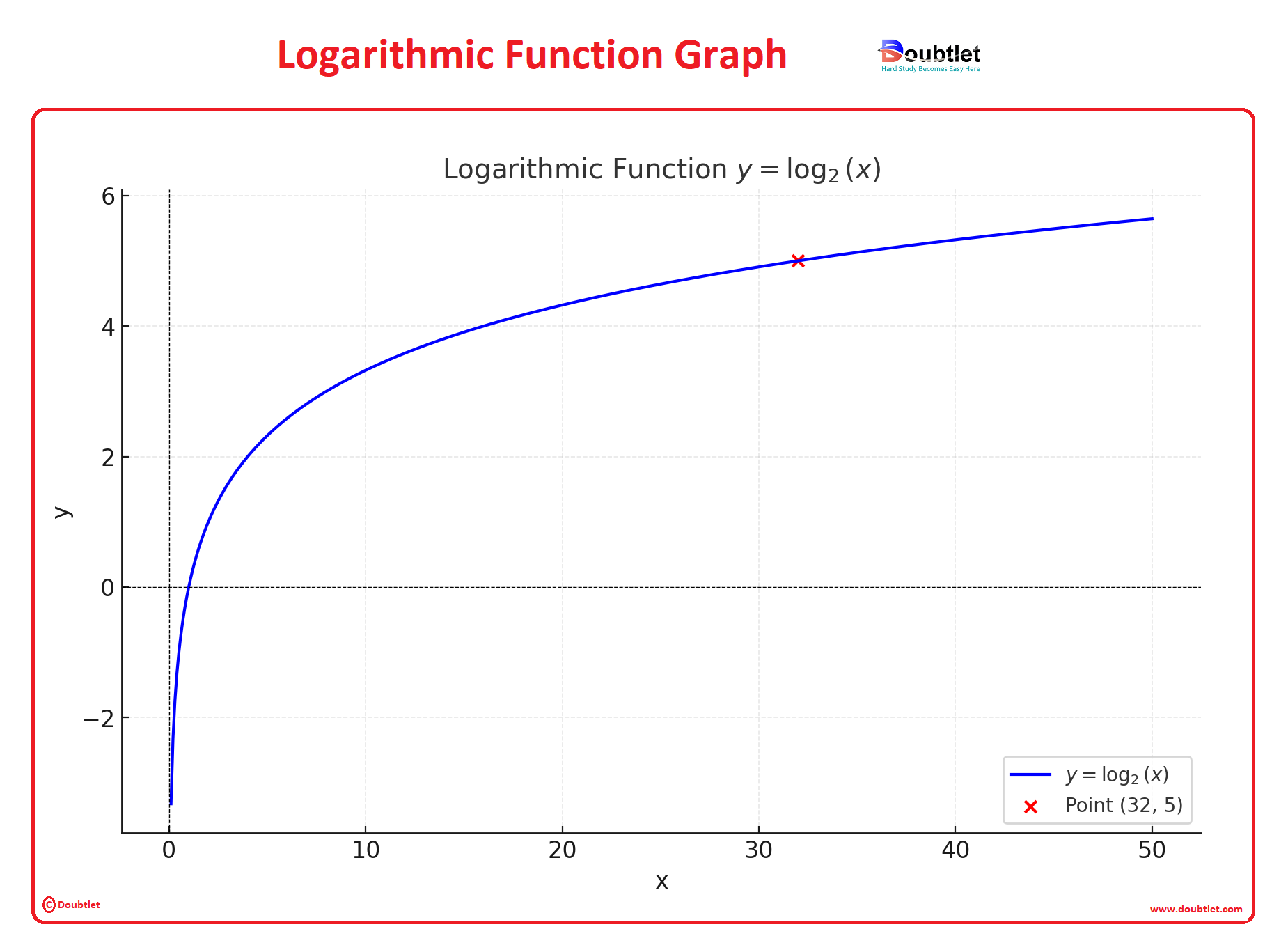
Explanation of the Graph:
-
Blue Curve ():
- Represents the base- logarithmic function.
- As increases, grows slowly, reflecting the logarithmic growth.
-
Red Point :
- Highlights the solution to the example: .
- This shows that , confirming the logarithmic relationship.
-
Axes:
- The -axis reflects the domain of the logarithmic function.
- The -axis shows the output values of the logarithm.
Key Insights:
- Logarithmic functions grow much slower than linear or exponential functions.
- The graph visually demonstrates the relationship between the base, exponent, and result in a logarithmic context.
4. Why Choose Our Logarithm Calculator?
Our calculator page provides a user-friendly interface that makes it accessible to both students and professionals. You can quickly input your square matrix and obtain the matrix of minors within a fraction of a second.
Our calculator saves you valuable time and effort. You no longer need to manually calculate each cofactor, making complex matrix operations more efficient.
Our calculator ensures accurate results by performing calculations based on established mathematical formulas and algorithms. It eliminates the possibility of human error associated with manual calculations.
Our calculator can handle all input values like integers, fractions, or any real number.
Alongside this calculator, our website offers additional calculators related to Pre-algebra, Algebra, Precalculus, Calculus, Coordinate geometry, Linear algebra, Chemistry, Physics, and various algebraic operations. These calculators can further enhance your understanding and proficiency.
5. A video based on how to Evaluate the Logarithm .
6. How to use this calculator?
Using the Logarithm Calculator is simple:
- Input Values: Enter the base and the number for which you want to calculate the logarithm.
- Click Calculate: Instantly view the logarithmic results.
- Analyze Results: Use the output for solving equations, analyzing data, or other applications.
This tool handles both individual and batch calculations efficiently.
7. Solved Examples on Logarithm
Example 1: Find :
Solution:
- .
- Solve .
- , because .
Example 2: Tabular Data:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Steps:
-
Enter the values into the calculator.
-
Compute logarithms for each row.
- .
- .
- .
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is a logarithm?
A logarithm is the exponent to which a base must be raised to produce a given number.
Q2. What is the difference between and ?
uses base , while (natural logarithm) uses base .
Q3. Is this calculator free?
Yes, our Logarithm Calculator is completely free.
Q4. Can I use it for non-integer bases?
Yes, the calculator supports any positive base.
Q5. Does it handle large datasets?
Absolutely, it’s optimized for batch calculations with tabular data.
Q6. Can I calculate logarithms for negative numbers?
No, logarithms are undefined for negative numbers.
Q7. Is it mobile-friendly?
Yes, the calculator works seamlessly on any device.
Q8. Can I export the results?
Yes, the output can be downloaded for further analysis or reporting.
9. What are the real-life applications?
Logarithms are used in various fields, such as:
- Mathematics: Solve exponential equations and model growth or decay.
- Physics: Analyze sound intensity (decibels) and radioactive decay.
- Engineering: Compute signal strength and system efficiency.
- Computer Science: Optimize algorithms and data structures.
- Finance: Calculate compound interest and growth rates.
Fictional Anecdote: Michael, a software engineer, uses our Logarithm Calculator to optimize algorithms for large datasets. By simplifying complex logarithmic calculations, he improves system efficiency by .
10. Conclusion
The Logarithm Calculator is an indispensable tool for simplifying mathematical computations, analyzing data, and solving equations. With its accuracy, speed, and user-friendly interface, it’s perfect for students, educators, and professionals alike.
Ready to make logarithms easy? Try our Logarithm Calculator today and experience the power of simplified calculations!
If you have any suggestions regarding the improvement of the content of this page, please write to me at My Official Email Address: doubt@doubtlet.com
Are you Stuck on homework, assignments, projects, quizzes, labs, midterms, or exams?
To get connected to our tutors in real time. Sign up and get registered with us.
FOIL Method Calculator
Fraction to Percent Calculator
Cube Root Calculator
Exponential Function Calculator
Rational Zeros Theorem Calculator
BMI Calculator
8th Pay Commission Salary Calculator









