









Rational Zeros Theorem Calculator
This calculator will help you to find all possible rational roots of the given polynomial with the steps shown.Related Calculator:Remainder Theorem Calculator
Loading...

Neetesh Kumar | February 7, 2025
Share this Page on:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
- 1. Introduction to the Rational Zeros Theorem Calculator
- 2. What is the Formulae used?
- 3. How do I find the Rational Zeros Theorem?
- 4. Why Choose Our Rational Zeros Theorem Calculator?
- 5. A Video for explaining this concept
- 6. How to use this calculator?
- 7. Solved Examples on Rational Zeros Theorem
- 8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 9. What are the real-life applications?
- 10. Conclusion
Finding the rational zeros of a polynomial can be a tedious process, especially for higher-degree equations. The Rational Zeros Theorem provides a systematic way to identify possible rational roots, saving time and effort.
Our Rational Zeros Theorem Calculator automates this process, allowing students, teachers, and professionals to quickly find all possible rational zeros of a polynomial. Whether you're solving equations for algebra, calculus, or engineering applications, this tool helps you effortlessly determine rational roots.
1. Introduction to the Rational Zeros Theorem Calculator
The Rational Zeros Theorem is a mathematical rule that helps identify all possible rational roots of a polynomial equation. It is particularly useful when solving polynomials manually, as it narrows down potential solutions before applying methods like synthetic division or factoring.
Our Rational Zeros Theorem Calculator simplifies this process by:
- Listing all possible rational zeros of a polynomial.
- Filtering valid rational roots using synthetic division.
- Providing step-by-step solutions for better understanding.
This tool is perfect for students working on algebra problems or professionals dealing with mathematical modeling and computations.
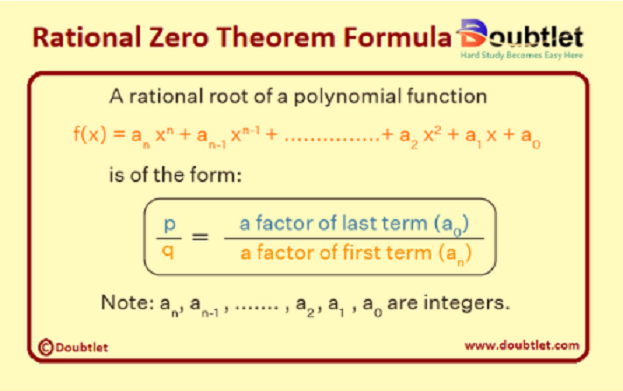
2. What is the Formulae used?
Rational Zeros Theorem:
where:
- is the leading coefficient (coefficient of the highest-degree term).
- is the constant term.
The Rational Zeros Theorem states that any rational solution must satisfy:
This means all possible rational zeros are given by:
By systematically testing these values, we can find the actual rational zeros of the polynomial.
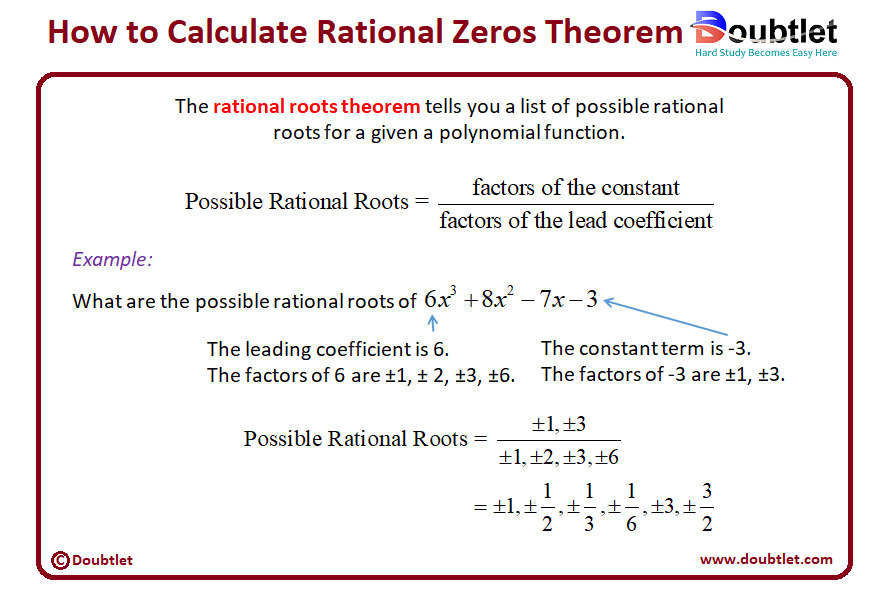
3. How Do I Find the Rational Zeros Using the Theorem?
Step 1: Identify Coefficients
Extract and from the given polynomial.
Step 2: List Factors
Find all integer factors of (constant term) and (leading coefficient).
Step 3: Form Possible Rational Zeros
Write all possible fractions where:
- is a factor of .
- is a factor of .
Step 4: Test Rational Zeros
Substitute each candidate into the polynomial and check which ones satisfy .
Example Calculation:
Find the rational zeros of:
Step 1: Identify Coefficients
- Leading coefficient
- Constant term
Step 2: List Factors
- Factors of :
- Factors of :
Step 3: Form Possible Rational Zeros
Step 4: Test Rational Zeros
By substituting, we find that and satisfy , meaning they are rational zeros of the polynomial.
For complex polynomials, our calculator performs these steps automatically!
4. Why choose our Rational Zeros Theorem Calculator?
Our calculator page provides a user-friendly interface that makes it accessible to both students and professionals. You can quickly input your square matrix and obtain the matrix of minors within a fraction of a second.
Our calculator saves you valuable time and effort. You no longer need to manually calculate each cofactor, making complex matrix operations more efficient.
Our calculator ensures accurate results by performing calculations based on established mathematical formulas and algorithms. It eliminates the possibility of human error associated with manual calculations.
Our calculator can handle all input values like integers, fractions, or any real number.
Alongside this calculator, our website offers additional calculators related to Pre-algebra, Algebra, Precalculus, Calculus, Coordinate geometry, Linear algebra, Chemistry, Physics, and various algebraic operations. These calculators can further enhance your understanding and proficiency.
5. A video based on how to Evaluate the Rational Zeros Theorem.
6. How to use this calculator?
Using the Rational Zeros Theorem Calculator is simple:
- Enter the Polynomial Equation: Input coefficients of the polynomial.
- Click Calculate: Instantly generate possible rational zeros.
- Analyze the Results: Identify actual rational solutions using synthetic division.
This tool eliminates errors and makes polynomial root-finding fast and accurate!
7. Solved Examples on Rational Zeros Theorem
Example 1: Find the Rational Zeros of a Cubic Polynomial
Find the rational zeros of the polynomial:
Step 1: Identify Coefficients
- Leading coefficient
- Constant term
Step 2: List Factors
- Factors of 6 (constant term):
- Factors of 1 (leading coefficient):
Step 3: Form Possible Rational Zeros
Possible rational zeros are:
Step 4: Test Rational Zeros Using Substitution
Testing
Since , is a rational zero.
Testing
Since , is also a rational zero.
Testing
Since , is another rational zero.
Final Answer:
The rational zeros of are:
Example 2: Find the Rational Zeros of a Quartic Polynomial
Find the rational zeros of:
Step 1: Identify Coefficients
- Leading coefficient
- Constant term
Step 2: List Factors
- Factors of (constant term):
- Factors of (leading coefficient):
Step 3: Form Possible Rational Zeros
After simplification, the unique possible rational zeros are:
Step 4: Test Rational Zeros Using Substitution
By substituting and using synthetic division, we find:
- is a zero.
- is a zero.
Final Answer:
The rational zeros of are:
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the Rational Zeros Theorem?
It helps find all possible rational solutions of a polynomial equation using factors of the constant and leading coefficient.
Q2. Can this theorem find all real solutions?
No, it only finds rational zeros. Some polynomials have irrational or complex roots.
Q3. What if my polynomial has no rational zeros?
If none of the candidates satisfy , then the polynomial has only irrational or complex solutions.
Q4. Can I use this for higher-degree polynomials?
Yes! Our calculator supports all degrees of polynomials.
Q5. Is this calculator free?
Yes, it's free and accessible from any device.
Q6. Does it work for non-integer coefficients?
The Rational Zeros Theorem only applies to integer coefficient polynomials.
Q7. Can I export the results?
Yes, results can be saved or copied for further analysis.
Q8. Is this tool mobile-friendly?
Yes, it works seamlessly on desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
9. What Are the Real-Life Applications?
The Rational Zeros Theorem is useful in:
- Algebra & Calculus: Finding exact solutions to equations.
- Engineering: Modeling real-world problems with polynomials.
- Physics: Analyzing motion and wave equations.
- Finance & Economics: Solving equations in growth models.
10. Conclusion
The Rational Zeros Theorem Calculator is a must-have tool for solving polynomial equations quickly and accurately. Whether you're a student or a professional, this tool saves time, reduces errors, and helps you master polynomials effortlessly.
Ready to simplify polynomial root-finding? Try our Rational Zeros Theorem Calculator now!
If you have any suggestions regarding the improvement of the content of this page, please write to me at My Official Email Address: doubt@doubtlet.com
Are you Stuck on homework, assignments, projects, quizzes, labs, midterms, or exams?
To get connected to our tutors in real time. Sign up and get registered with us.
Cube Root Calculator
Exponential Function Calculator
BMI Calculator
8th Pay Commission Salary Calculator
Age Calculator
Simple Interest Calculator
Compound Interest Calculator









