









Remainder Theorem Calculator
This calculator will help you to calculate the remainder while dividing two polynomials with the steps shown.Related Calculator:Rational Zeros Theorem Calculator
Loading...
Loading...

Neetesh Kumar | February 18, 2025
Share this Page on:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
- 1. Introduction to the Remainder Theorem Calculator
- 2. What is the Formulae used?
- 3. How do I find the Remainder Theorem?
- 4. Why choose our Remainder Theorem Calculator?
- 5. A Video for explaining this concept
- 6. How to use this calculator?
- 7. Solved Examples on Remainder Theorem.
- 8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 9. What are the real-life applications?
- 10. Conclusion
Solving polynomial division problems manually can be tedious, but the Remainder Theorem simplifies the process. Instead of performing full polynomial division, you can quickly find the remainder when a polynomial is divided by a linear divisor using this theorem.
Our Remainder Theorem Calculator makes it even easier! Just enter your polynomial and divisor, and the tool instantly provides the remainder. Whether you’re a student, teacher, or mathematician, this calculator helps you save time and avoid calculation errors.
1. Introduction to the Remainder Theorem Calculator
The Remainder Theorem states that when a polynomial is divided by , the remainder is simply .
Our Remainder Theorem Calculator is designed to:
- Instantly find the remainder of a polynomial division
- Simplify complex polynomial calculations
- Help students learn and practice algebra efficiently
- Save time compared to long division or synthetic division
If you’re solving algebra problems, preparing for exams, or working with polynomial functions, this calculator is an essential tool!
2. What is the Formulae used?
The Remainder Theorem Formula states:
Where:
- is the polynomial
- is the divisor
- is the value obtained by setting the divisor
- is the remainder when is divided by
Example Formula Application:
For a polynomial:
If divided by :
- Set
- Compute :
- Remainder = 31
Our calculator automates this instantly, eliminating the need for manual calculations.
What is the Remainder Theorem?
The remainder theorem states that when a polynomial is divided by a linear polynomial , then the remainder is equal to . The remainder theorem enables us to calculate the remainder of the division of any polynomial by a linear polynomial, without actually carrying out the steps of the long division.
Note that the degree of the remainder polynomial is always 1 less than the degree of the divisor polynomial. Using this fact, when any polynomial is divided by a linear polynomial (whose degree is 1), the remainder must be a constant (whose degree is 0).
Remainder Theorem Statement and Proof
According to the remainder theorem, when a polynomial (whose degree is greater than or equal to 1) is divided by a linear polynomial , the remainder is given by .
i.e., to find the remainder, follow the steps below:
- Find the zero of the linear polynomial by setting it to zero.
i.e., . - Then just substitute it in the given polynomial. The result would give the remainder.
Here is the remainder theorem formula depending on the type of divisor (linear polynomial).
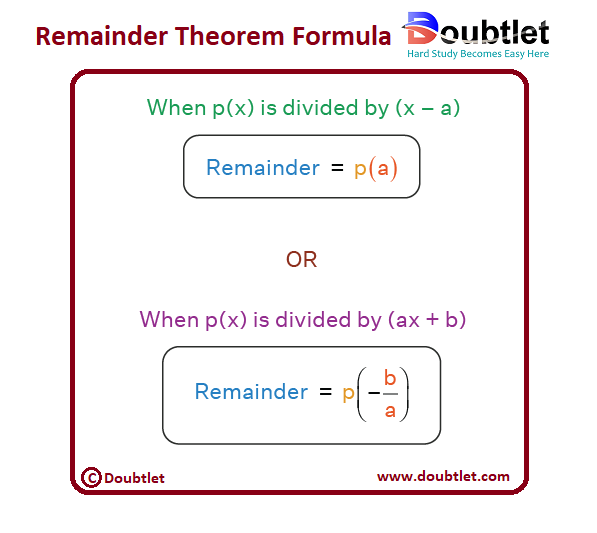
Similarly, we can extend the remainder theorem for different types of linear polynomials as follows:
- The remainder when is divided by is
(∵ ). - The remainder when is divided by is
(∵ ). - The remainder when is divided by is
(∵ ). - The remainder when is divided by is
(∵ ).
Proof of Remainder Theorem
Let us assume that and are the quotient and the remainder respectively when a polynomial is divided by a linear polynomial .
By the division algorithm,
Using this,
Substituting :
i.e., the remainder = .
Hence, proved.
3. How Do I Find the Remainder Using the Theorem?
Step 1: Identify the Polynomial and Divisor
Write down the polynomial and divisor .
Step 2: Solve for in the Divisor
Set and solve for to find the value of .
Step 3: Substitute into
Evaluate the polynomial at to get the remainder.
Step 4: Interpret the Result
- If remainder , then is a factor of the polynomial.
- If remainder , the remainder tells you what’s left after division.
For a faster solution, enter values into our Remainder Theorem Calculator, and get instant results!
Remainder Theorem for Polynomials
The remainder can be easily found when a polynomial is divided by a linear polynomial. To find it, just substitute the zero of the linear polynomial in the dividend polynomial.
To see how it works in the case of polynomials, let us consider the following example with two polynomials:
Dividend,
Divisor:
Let us find the remainder in two ways:
- Using the long division
- Using the remainder theorem
Let us observe whether both answers are the same.
By using the long division of polynomials:
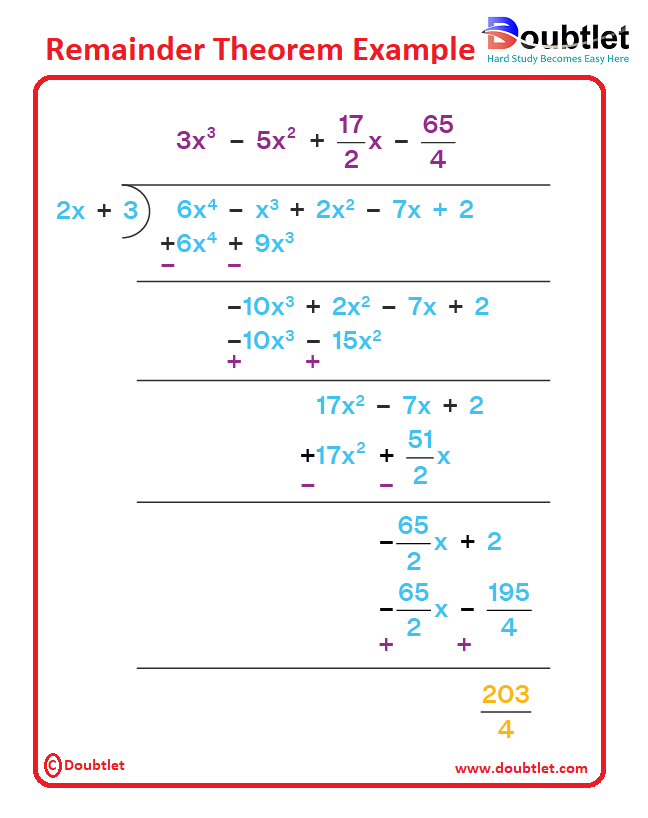
On dividing polynomials, the remainder that we have got is, .
Now, let’s find the remainder by using the remainder theorem.
i.e., first we find the zero of the linear polynomial:
and then substitute it in the given polynomial. Then we get:
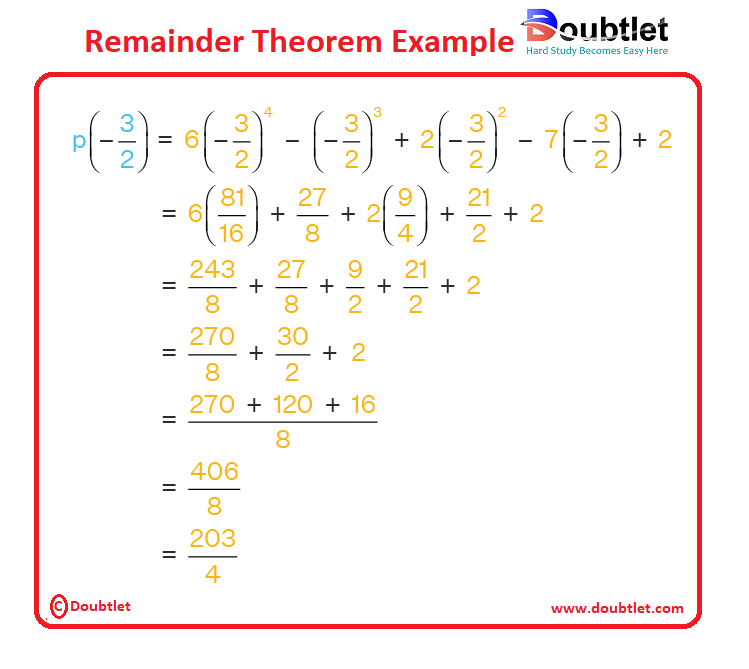
We have got the remainder to be and the answer matched with the remainder found using the long division.
Hence, the remainder theorem works wonders for polynomials.
4. Why Choose Our Remainder Theorem Calculator?
Our calculator page provides a user-friendly interface that makes it accessible to both students and professionals. You can quickly input your square matrix and obtain the matrix of minors within a fraction of a second.
Our calculator saves you valuable time and effort. You no longer need to manually calculate each cofactor, making complex matrix operations more efficient.
Our calculator ensures accurate results by performing calculations based on established mathematical formulas and algorithms. It eliminates the possibility of human error associated with manual calculations.
Our calculator can handle all input values like integers, fractions, or any real number.
Alongside this calculator, our website offers additional calculators related to Pre-algebra, Algebra, Precalculus, Calculus, Coordinate geometry, Linear algebra, Chemistry, Physics, and various algebraic operations. These calculators can further enhance your understanding and proficiency.
5. A video based on how to Evaluate the Remainder Theorem.
6. How to use this calculator?
Using the Remainder Theorem Calculator is simple:
-
Enter the polynomial (e.g., ).
-
Enter the divisor (e.g., ).
-
Click Calculate – The tool instantly computes:
- The remainder
- A step-by-step explanation
No more tedious calculations just fast and accurate results!
7. Solved Examples on Remainder Theorem.
Example 1: Finding the Remainder of a Polynomial Division
Given:
Divisor:
Step 1: Find from
Step 2: Compute
Remainder =
Example 2: Checking if a Polynomial is Divisible
Given:
Divisor:
Step 1: Compute
Since the remainder is 0, is a factor of .
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the Remainder Theorem?
The Remainder Theorem states that the remainder when a polynomial is divided by is simply .
Q2. How is the remainder calculated?
You substitute into and compute .
Q3. Can I use this theorem for all polynomials?
Yes, it works for quadratic, cubic, quartic, and higher-degree polynomials.
Q4. What if the remainder is 0?
It means that is a factor of .
Q5. Does this work for non-monic polynomials?
Yes, it works for any polynomial, even if the leading coefficient isn’t 1.
Q6. What if the divisor isn’t in the form ?
The theorem only works when dividing by a linear divisor of the form .
Q7. Can this calculator handle large polynomials?
Yes! It works for higher-degree polynomials instantly.
Q8. Is this calculator free?
Yes, our Remainder Theorem Calculator is 100% free to use!
9. What Are the Real-Life Applications?
The Remainder Theorem is used in:
- Algebra & Calculus: Simplifying polynomial division.
- Engineering & Physics: Modeling complex systems.
- Computer Science: Polynomial time algorithms.
- Education: Teaching students polynomial concepts.
10. Conclusion
The Remainder Theorem Calculator is a fast, reliable, and easy-to-use tool for polynomial division.
Whether you’re solving homework problems or conducting research, this calculator saves time and effort.
- Try our Remainder Theorem Calculator today and simplify your polynomial problems instantly!
If you have any suggestions regarding the improvement of the content of this page, please write to me at My Official Email Address: doubt@doubtlet.com
Are you Stuck on homework, assignments, projects, quizzes, labs, midterms, or exams?
To get connected to our tutors in real time. Sign up and get registered with us.
Nth Root calculator
Exponential Function Calculator
Rational Zeros Theorem Calculator
Degree and Leading Coefficient Calculator
BMI Calculator
Period Calculator
8th Pay Commission Salary Calculator
Age Calculator









