Trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent, etc.) describe the relationships between the angles and sides of a right triangle, while
Neetesh Kumar | May 17, 2024
\space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space \space Share this Page on:
1. Relation between Degree, Grade, and Radian:
D 90 = G 100 = 2 C π \frac{D}{90} = \frac{G}{100} = \frac{2C}{\pi} 90 D = 100 G = π 2 C 180 π \frac{180}{\pi} π 180 ≈ \approx ≈ 5 7 o 1 7 ′ 1 5 ′ ′ 57^o17'15'' 5 7 o 1 7 ′ 1 5 ′′ π 180 \frac{\pi}{180} 180 π ≈ \approx ≈
2. General Trigonometric Identities:
( a ) \bold{(a)} ( a ) 2 θ ^2\theta 2 θ 2 θ = 1 ^2\theta = 1 2 θ = 1 ( b ) \bold{(b)} ( b ) 2 θ ^2\theta 2 θ 2 θ = 1 ^2\theta = 1 2 θ = 1 ( c ) \bold{(c)} ( c ) 2 θ ^2\theta 2 θ 2 θ = 1 ^2\theta = 1 2 θ = 1 ( d ) \bold{(d)} ( d ) θ \theta θ θ = k ⇒ \theta = k \Rightarrow θ = k ⇒ θ \theta θ θ = 1 k ⇒ 2 S e c θ = k + 1 k \theta = \frac{1}{k} \Rightarrow 2Sec\theta = k + \frac{1}{k} θ = k 1 ⇒ 2 S ec θ = k + k 1 ( e ) \bold{(e)} ( e ) θ \theta θ θ = k ⇒ \theta = k \Rightarrow θ = k ⇒ θ \theta θ θ = 1 k ⇒ 2 C o s e c θ = k + 1 k \theta = \frac{1}{k} \Rightarrow 2Cosec\theta = k + \frac{1}{k} θ = k 1 ⇒ 2 C osec θ = k + k 1
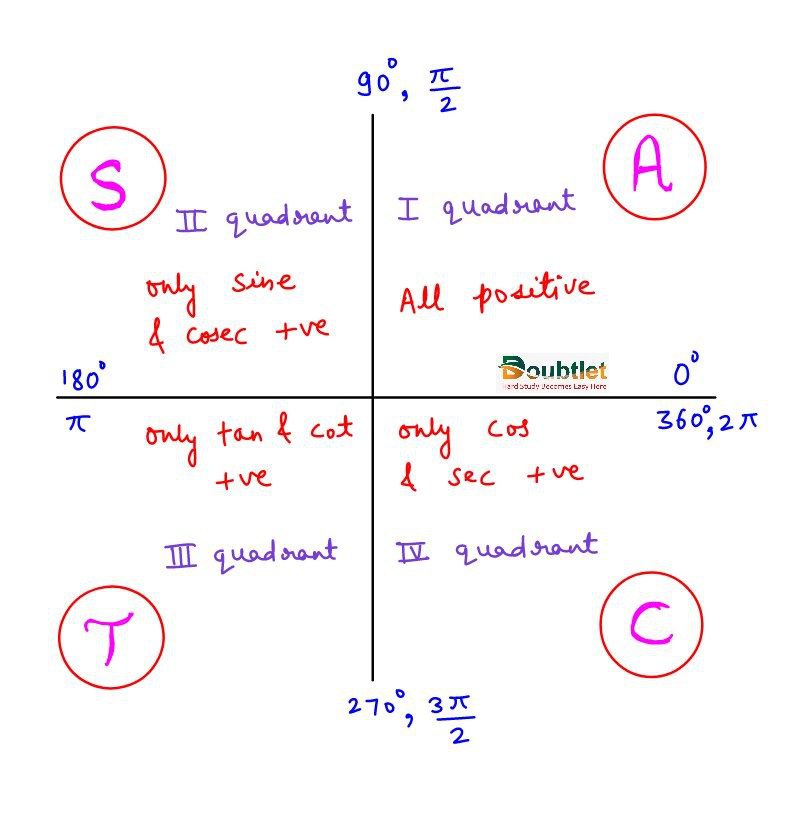
3. Sign Convention in different Quadrants:
4. Trigonometric Functions of Allied angles:
( a ) \bold{(a)} ( a ) 2 n π + θ 2n\pi + \theta 2 nπ + θ θ \theta θ 2 n π + θ 2n\pi + \theta 2 nπ + θ θ \theta θ ∈ \in ∈ ( b ) \bold{(b)} ( b )
Sin(− θ -\theta − θ − - − θ \theta θ
Cos(− θ -\theta − θ θ \theta θ
Sin(90 − θ 90-\theta 90 − θ θ \theta θ
Cos(90 − θ 90-\theta 90 − θ θ \theta θ
Sin(90 + θ 90+\theta 90 + θ θ \theta θ
Cos(90 + θ 90+\theta 90 + θ θ \theta θ
Sin(180 − θ 180-\theta 180 − θ θ \theta θ
Cos(180 − θ 180-\theta 180 − θ − - − θ \theta θ
Sin(180 + θ 180+\theta 180 + θ − - − θ \theta θ
Cos(180 + θ 180+\theta 180 + θ − - − θ \theta θ
Sin(270 − θ 270-\theta 270 − θ − - − θ \theta θ
Cos(270 − θ 270-\theta 270 − θ − - − θ \theta θ
Sin(270 + θ 270+\theta 270 + θ − - − θ \theta θ
Cos(270 + θ 270+\theta 270 + θ θ \theta θ
( c ) \bold{(c)} ( c ) ( n π ) = 0 ; C o s ( n π ) = ( − 1 ) n ; t a n ( n π ) = 0 (n\pi)=0; Cos(n\pi) = (-1)^n; tan(n\pi)=0 ( nπ ) = 0 ; C os ( nπ ) = ( − 1 ) n ; t an ( nπ ) = 0 ∈ \in ∈ ( d ) \bold{(d)} ( d ) ( 2 n + 1 ) π 2 = ( − 1 ) n ; (2n+1)\frac{\pi}{2} = (-1)^n; ( 2 n + 1 ) 2 π = ( − 1 ) n ; ( 2 n + 1 ) π 2 = 0 (2n+1)\frac{\pi}{2} = 0 ( 2 n + 1 ) 2 π = 0 ∈ \in ∈
5. Important Trigonometric Formulae:
Sin(A + B) = SinA.CosB + CosA.SinB
Sin(A - B) = SinA.CosB - CosA.SinB
Cos(A + B) = CosA.CosB - SinA.SinB
Cos(A - B) = CosA.CosB + SinA.SinB
tan(A + B) = t a n A + t a n B 1 − t a n A . t a n B \frac{tanA + tanB}{1-tanA.tanB} 1 − t an A . t an B t an A + t an B
tan(A - B) = t a n A − t a n B 1 + t a n A . t a n B \frac{tanA - tanB}{1+tanA.tanB} 1 + t an A . t an B t an A − t an B
Cot(A+B) = C o t B . C o t A − 1 C o t B + C o t A \frac{CotB.CotA - 1}{CotB + CotA} C o tB + C o t A C o tB . C o t A − 1
Cot(A-B) = C o t B . C o t A + 1 C o t B − C o t A \frac{CotB.CotA + 1}{CotB - CotA} C o tB − C o t A C o tB . C o t A + 1
2SinA.CosB = Sin(A+B) + Sin(A-B)
2CosA.SinB = Sin(A+B) - Sin(A-B)
2CosA.CosB = Cos(A+B) + Cos(A-B)
2SinA.SinB = Cos(A-B) - Cos(A+B)
SinC + SinD = 2Sin( C + D 2 ) (\frac{C+D}{2}) ( 2 C + D ) ( C − D 2 ) (\frac{C-D}{2}) ( 2 C − D )
SinC - SinD = 2Cos( C + D 2 ) (\frac{C+D}{2}) ( 2 C + D ) ( C − D 2 ) (\frac{C-D}{2}) ( 2 C − D )
CosC + CosD = 2Cos( C + D 2 ) (\frac{C+D}{2}) ( 2 C + D ) ( C − D 2 ) (\frac{C-D}{2}) ( 2 C − D )
CosC - CosD = − - − ( C + D 2 ) (\frac{C+D}{2}) ( 2 C + D ) ( C − D 2 ) (\frac{C-D}{2}) ( 2 C − D )
Sin2 θ = 2\theta = 2 θ = θ \theta θ θ = 2 t a n θ 1 + t a n 2 θ \theta = \frac{2tan\theta}{1+tan^2\theta} θ = 1 + t a n 2 θ 2 t an θ
Cos2 θ = 2\theta= 2 θ = 2 θ − ^2\theta - 2 θ − 2 θ ^2\theta 2 θ 2 θ − 1 = 1 − 2 ^2\theta - 1 = 1 - 2 2 θ − 1 = 1 − 2 2 θ = 1 − t a n 2 θ 1 + t a n 2 θ ^2\theta = \frac{1-tan^2\theta}{1+tan^2\theta} 2 θ = 1 + t a n 2 θ 1 − t a n 2 θ
1 - Cos2 θ 2\theta 2 θ 2 θ ^2\theta 2 θ θ \theta θ 1 − C o s 2 θ 2 \frac{1-Cos2\theta}{2} 2 1 − C os 2 θ
tanθ = 1 − C o s 2 θ S i n 2 θ = S i n 2 θ 1 + C o s 2 θ \theta = \frac{1-Cos2\theta}{Sin2\theta} = \frac{Sin2\theta}{1+Cos2\theta} θ = S in 2 θ 1 − C os 2 θ = 1 + C os 2 θ S in 2 θ
tan2 θ = 2 t a n θ 1 − t a n 2 θ 2\theta = \frac{2tan\theta}{1-tan^2\theta} 2 θ = 1 − t a n 2 θ 2 t an θ
Sin3 θ 3\theta 3 θ θ \theta θ 3 θ ^3\theta 3 θ
Cos3 θ 3\theta 3 θ 3 θ ^3\theta 3 θ θ \theta θ
Sinθ \theta θ ( 60 − θ ) (60-\theta) ( 60 − θ ) ( 60 + θ ) = 1 4 S i n ( 3 θ ) (60+\theta) = \frac{1}{4}Sin(3\theta) ( 60 + θ ) = 4 1 S in ( 3 θ )
Cosθ \theta θ ( 60 − θ ) (60-\theta) ( 60 − θ ) ( 60 + θ ) = 1 4 C o s ( 3 θ ) (60+\theta) = \frac{1}{4}Cos(3\theta) ( 60 + θ ) = 4 1 C os ( 3 θ )
tanθ \theta θ ( 60 − θ ) (60-\theta) ( 60 − θ ) ( 60 + θ ) = t a n ( 3 θ ) (60+\theta) = tan(3\theta) ( 60 + θ ) = t an ( 3 θ )
cotθ \theta θ ( 60 − θ ) (60-\theta) ( 60 − θ ) ( 60 + θ ) = c o t ( 3 θ ) (60+\theta) = cot(3\theta) ( 60 + θ ) = co t ( 3 θ )
Sin2 θ ^2\theta 2 θ 2 ( 60 − θ ) ^2(60-\theta) 2 ( 60 − θ ) 2 ( 60 + θ ) = 3 2 ^2(60+\theta) = \frac{3}{2} 2 ( 60 + θ ) = 2 3
Cos2 θ ^2\theta 2 θ 2 ( 60 − θ ) ^2(60-\theta) 2 ( 60 − θ ) 2 ( 60 + θ ) = 3 2 ^2(60+\theta) = \frac{3}{2} 2 ( 60 + θ ) = 2 3
tan3 θ = 3 t a n θ − t a n 3 θ 1 − 3 t a n 2 θ 3\theta = \frac{3tan\theta - tan^3\theta}{1-3tan^2\theta} 3 θ = 1 − 3 t a n 2 θ 3 t an θ − t a n 3 θ
Sin2 A ^2A 2 A 2 B ^2B 2 B 2 ^2 2 2 ^2 2
Cos2 A ^2A 2 A 2 B ^2B 2 B
Sin(A+B+C) = SinA.CosB.CosC + SinB.CosA.CosC + SinC.CosA.CosB - SinA.SinB.SinC
Cos(A+B+C) = CosA.CosB.CosC - SinA.SinB.CosC - SinA.CosB.SinC - CosA.SinB.SinC
tan(A+B+C) = t a n A + t a n B + t a n C − t a n A . t a n B . t a n C 1 − t a n A . t a n B − t a n B t a n C − t a n C t a n A \frac{tanA + tanB + tanC - tanA.tanB.tanC}{1-tanA.tanB-tanBtanC-tanCtanA} 1 − t an A . t an B − t an Bt an C − t an Ct an A t an A + t an B + t an C − t an A . t an B . t an C
If tanA + tanB + tanC = tanA.tanB.tanC, then A + B + C = n π , n ∈ I n\pi, n \in I nπ , n ∈ I
If tanA.tanB + tanB.tanC + tanC.tanA = 1, then A + B + C = ( 2 n + 1 ) π 2 , n ∈ I (2n+1)\frac{\pi}{2}, n \in I ( 2 n + 1 ) 2 π , n ∈ I
Cosθ \theta θ 2 θ 2\theta 2 θ 4 θ 4\theta 4 θ ( 2 n − 1 θ ) = S i n ( 2 n θ ) 2 n S i n θ (2^{n-1}\theta) = \frac{Sin(2^n \theta)}{2^n Sin\theta} ( 2 n − 1 θ ) = 2 n S in θ S in ( 2 n θ )
CotA - tanA = 2Cot2A
Sinα \alpha α ( α + β ) (\alpha + \beta) ( α + β ) ( α + 2 β ) (\alpha + 2\beta) ( α + 2 β ) ( α + ( n − 1 ) ‾ β ) (\alpha + \overline{(n-1)}\beta) ( α + ( n − 1 ) β ) S i n ( α + ( n − 1 2 ) β ) S i n ( n β 2 ) S i n ( β 2 ) \frac{Sin(\alpha + (\frac{n-1}{2})\beta)Sin(\frac{n\beta}{2})}{Sin(\frac{\beta}{2})} S in ( 2 β ) S in ( α + ( 2 n − 1 ) β ) S in ( 2 n β )
Cosα \alpha α ( α + β ) (\alpha + \beta) ( α + β ) ( α + 2 β ) (\alpha + 2\beta) ( α + 2 β ) ( α + ( n − 1 ) ‾ β ) (\alpha + \overline{(n-1)}\beta) ( α + ( n − 1 ) β ) C o s ( α + ( n − 1 2 ) β ) S i n ( n β 2 ) S i n ( β 2 ) \frac{Cos(\alpha + (\frac{n-1}{2})\beta)Sin(\frac{n\beta}{2})}{Sin(\frac{\beta}{2})} S in ( 2 β ) C os ( α + ( 2 n − 1 ) β ) S in ( 2 n β )
6. Some special angles value for Trigonometric Ratios:
Sin18o = 5 − 1 4 = C o s 7 2 o = S i n ( π 10 ) ^o = \frac{\sqrt{5}-1}{4} = Cos72^o = Sin(\frac{\pi}{10}) o = 4 5 − 1 = C os 7 2 o = S in ( 10 π )
Cos36o = 5 + 1 4 = S i n 5 4 o = S i n ( π 5 ) ^o = \frac{\sqrt{5}+1}{4} = Sin54^o = Sin(\frac{\pi}{5}) o = 4 5 + 1 = S in 5 4 o = S in ( 5 π )
Sin15o = 3 − 1 2 2 = C o s 7 5 o = S i n ( π 12 ) ^o = \frac{\sqrt{3}-1}{2\sqrt{2}} = Cos75^o = Sin(\frac{\pi}{12}) o = 2 2 3 − 1 = C os 7 5 o = S in ( 12 π )
Cos15o = 3 + 1 2 2 = S i n 7 5 o = C o s ( π 12 ) ^o = \frac{\sqrt{3}+1}{2\sqrt{2}} = Sin75^o = Cos(\frac{\pi}{12}) o = 2 2 3 + 1 = S in 7 5 o = C os ( 12 π )
tan15o = 2 − 3 = 3 − 1 3 + 1 = C o t ( 5 π 12 ) = t a n ( π 12 ) ^o = 2 - \sqrt{3} = \frac{\sqrt{3} - 1}{\sqrt{3} + 1} = Cot(\frac{5\pi}{12}) = tan(\frac{\pi}{12}) o = 2 − 3 = 3 + 1 3 − 1 = C o t ( 12 5 π ) = t an ( 12 π )
tan75o = 2 + 3 = 3 + 1 3 − 1 = C o t ( π 12 ) = t a n ( 5 π 12 ) ^o = 2 + \sqrt{3} = \frac{\sqrt{3} + 1}{\sqrt{3} - 1} = Cot(\frac{\pi}{12}) = tan(\frac{5\pi}{12}) o = 2 + 3 = 3 − 1 3 + 1 = C o t ( 12 π ) = t an ( 12 5 π )
tan(22.5)o = 2 − 1 = c o t ( 67.5 ) o = C o t ( 3 π 8 ) = t a n ( π 8 ) ^o = \sqrt{2} - 1 = cot(67.5)^o = Cot(\frac{3\pi}{8}) = tan(\frac{\pi}{8}) o = 2 − 1 = co t ( 67.5 ) o = C o t ( 8 3 π ) = t an ( 8 π )
tan(67.5)o = 2 + 1 = c o t ( 22.5 ) o ^o = \sqrt{2} + 1 = cot(22.5)^o o = 2 + 1 = co t ( 22.5 ) o
I m p o r t a n t N o t e : \bold{Important \space Note:} Important Note : ( a ) \bold{(a)} ( a ) ( n − 2 ) (n - 2) ( n − 2 ) 18 0 o = ( n − 2 ) π . 180^o = (n - 2)\pi. 18 0 o = ( n − 2 ) π . ( b ) \bold{(b)} ( b ) ( n − 2 ) n \frac{(n-2)}{n} n ( n − 2 ) 18 0 o = ( n − 2 ) n π . 180^o = \frac{(n-2)}{n}\pi. 18 0 o = n ( n − 2 ) π . ( c ) \bold{(c)} ( c ) o = 2 π ^o = 2\pi o = 2 π
6. Maximum and Minimum values of Trigonometric Expressions:
( a ) \bold{(a)} ( a ) θ \theta θ θ \theta θ [ − a 2 + b 2 , a 2 + b 2 ] [-\sqrt{a^2+b^2}, \sqrt{a^2+b^2}] [ − a 2 + b 2 , a 2 + b 2 ] − a 2 + b 2 , a 2 + b 2 -\sqrt{a^2+b^2}, \sqrt{a^2+b^2} − a 2 + b 2 , a 2 + b 2
( b ) \bold{(b)} ( b ) a 2 t a n 2 θ + b 2 c o t 2 θ = 2 a b , a^2tan^2\theta + b^2cot^2\theta = 2ab, a 2 t a n 2 θ + b 2 co t 2 θ = 2 ab ,
( c ) \bold{(c)} ( c ) a 2 c o s 2 θ + b 2 s e c 2 θ a^2cos^2\theta + b^2sec^2\theta a 2 co s 2 θ + b 2 se c 2 θ a 2 s i n 2 θ + b 2 c o s e c 2 θ a^2sin^2\theta + b^2cosec^2\theta a 2 s i n 2 θ + b 2 cose c 2 θ ≥ \ge ≥ a 2 + b 2 a^2 + b^2 a 2 + b 2 ≤ \le ≤
R e l a t e d P a g e s : \color{red} \bold{Related \space Pages:} Related Pages : Trignometric Equation Formula Sheet Quadratic Equation Formula Sheet Operation on Matrices Matrices Formula Sheet










![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()