Neetesh Kumar | December 10, 2024
Calculus Homework Help
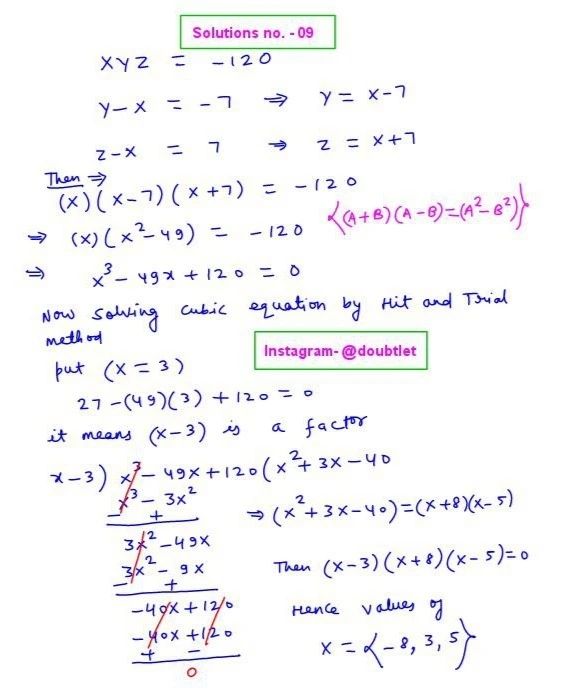
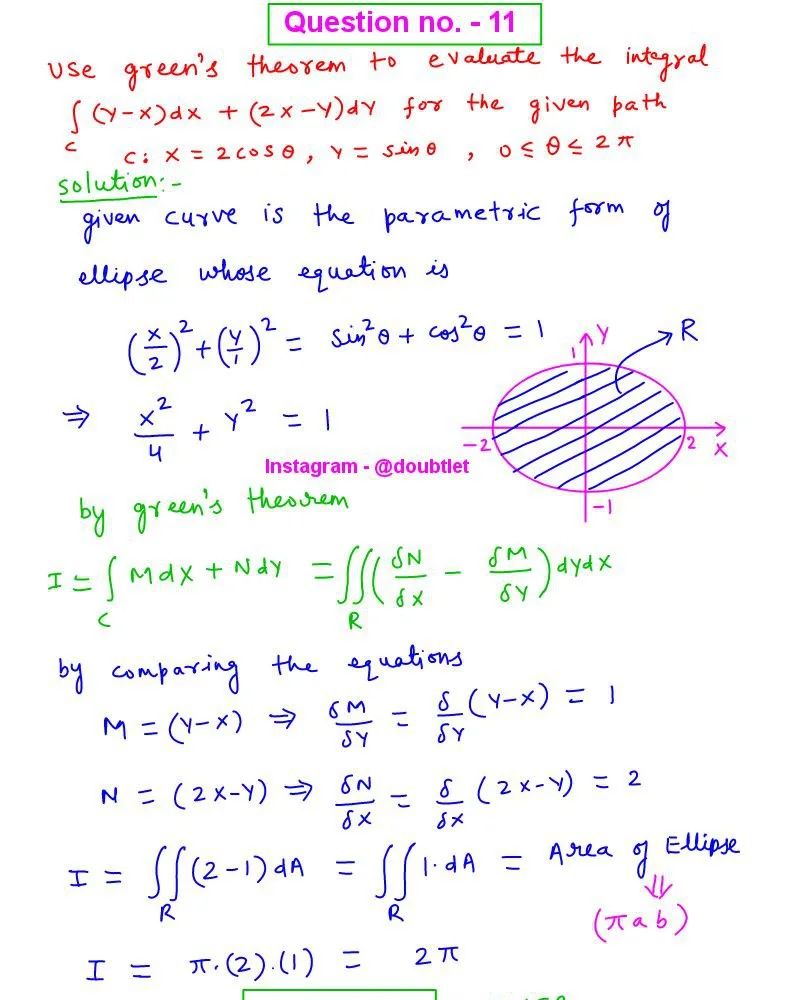
This is the solution to Math 132 Assignment: 7.5 Question Number 6 Contact me if you need help with Homework, Assignments, Tutoring Sessions, or Exams for STEM subjects. Testimonials or Vouches from here of the previous works I have done.
Get Homework Help
Step-by-step solution:
To evaluate ∫ 75 − 10 x − x 2 d x \int \sqrt{75 - 10x - x^2} \, dx ∫ 75 − 10 x − x 2 d x
Step 1: Simplify the quadratic expression
The quadratic inside the square root is 75 − 10 x − x 2 75 - 10x - x^2 75 − 10 x − x 2
Rewrite it in standard form:
− x 2 − 10 x + 75 -x^2 - 10x + 75 − x 2 − 10 x + 75
Factor out − 1 -1 − 1
− ( x 2 + 10 x − 75 ) - (x^2 + 10x - 75) − ( x 2 + 10 x − 75 )
Complete the square for x 2 + 10 x − 75 x^2 + 10x - 75 x 2 + 10 x − 75
Take half the coefficient of x x x ( 10 2 ) 2 = 25 \left(\frac{10}{2}\right)^2 = 25 ( 2 10 ) 2 = 25
Add and subtract 25 25 25
x 2 + 10 x − 75 = ( x 2 + 10 x + 25 ) − 25 − 75 = ( x + 5 ) 2 − 100 x^2 + 10x - 75 = (x^2 + 10x + 25) - 25 - 75 = (x + 5)^2 - 100 x 2 + 10 x − 75 = ( x 2 + 10 x + 25 ) − 25 − 75 = ( x + 5 ) 2 − 100
So the quadratic becomes:
75 − 10 x − x 2 = − ( ( x + 5 ) 2 − 100 ) = 100 − ( x + 5 ) 2 75 - 10x - x^2 = -\left((x + 5)^2 - 100\right) = 100 - (x + 5)^2 75 − 10 x − x 2 = − ( ( x + 5 ) 2 − 100 ) = 100 − ( x + 5 ) 2
Thus, the integral is:
∫ 75 − 10 x − x 2 d x = ∫ 100 − ( x + 5 ) 2 d x \int \sqrt{75 - 10x - x^2} \, dx = \int \sqrt{100 - (x + 5)^2} \, dx ∫ 75 − 10 x − x 2 d x = ∫ 100 − ( x + 5 ) 2 d x
Step 2: Substitution for the circle
The expression 100 − ( x + 5 ) 2 \sqrt{100 - (x + 5)^2} 100 − ( x + 5 ) 2 10 10 10
Use the substitution:
x + 5 = 10 sin ( θ ) , d x = 10 cos ( θ ) d θ x + 5 = 10 \sin(\theta), \quad dx = 10 \cos(\theta) \, d\theta x + 5 = 10 sin ( θ ) , d x = 10 cos ( θ ) d θ
Substitute into the integral:
∫ 100 − ( x + 5 ) 2 d x = ∫ 100 − 100 sin 2 ( θ ) ⋅ 10 cos ( θ ) d θ \int \sqrt{100 - (x + 5)^2} \, dx = \int \sqrt{100 - 100 \sin^2(\theta)} \cdot 10 \cos(\theta) \, d\theta ∫ 100 − ( x + 5 ) 2 d x = ∫ 100 − 100 sin 2 ( θ ) ⋅ 10 cos ( θ ) d θ
Simplify the square root using the Pythagorean identity 1 − sin 2 ( θ ) = cos 2 ( θ ) 1 - \sin^2(\theta) = \cos^2(\theta) 1 − sin 2 ( θ ) = cos 2 ( θ )
100 − 100 sin 2 ( θ ) = 100 cos 2 ( θ ) = 10 cos ( θ ) \sqrt{100 - 100 \sin^2(\theta)} = \sqrt{100 \cos^2(\theta)} = 10 \cos(\theta) 100 − 100 sin 2 ( θ ) = 100 cos 2 ( θ ) = 10 cos ( θ )
The integral becomes:
∫ 10 cos ( θ ) ⋅ 10 cos ( θ ) d θ = 100 ∫ cos 2 ( θ ) d θ \int 10 \cos(\theta) \cdot 10 \cos(\theta) \, d\theta = 100 \int \cos^2(\theta) \, d\theta ∫ 10 cos ( θ ) ⋅ 10 cos ( θ ) d θ = 100 ∫ cos 2 ( θ ) d θ
Step 3: Simplify cos 2 ( θ ) \cos^2(\theta) cos 2 ( θ )
Use the half-angle identity:
cos 2 ( θ ) = 1 + cos ( 2 θ ) 2 \cos^2(\theta) = \frac{1 + \cos(2\theta)}{2} cos 2 ( θ ) = 2 1 + c o s ( 2 θ )
Substitute into the integral:
100 ∫ cos 2 ( θ ) d θ = 100 ∫ 1 + cos ( 2 θ ) 2 d θ = 50 ∫ ( 1 + cos ( 2 θ ) ) d θ 100 \int \cos^2(\theta) \, d\theta = 100 \int \frac{1 + \cos(2\theta)}{2} \, d\theta = 50 \int (1 + \cos(2\theta)) \, d\theta 100 ∫ cos 2 ( θ ) d θ = 100 ∫ 2 1 + c o s ( 2 θ ) d θ = 50 ∫ ( 1 + cos ( 2 θ )) d θ
Split the integral:
50 ∫ ( 1 + cos ( 2 θ ) ) d θ = 50 ∫ 1 d θ + 50 ∫ cos ( 2 θ ) d θ 50 \int (1 + \cos(2\theta)) \, d\theta = 50 \int 1 \, d\theta + 50 \int \cos(2\theta) \, d\theta 50 ∫ ( 1 + cos ( 2 θ )) d θ = 50 ∫ 1 d θ + 50 ∫ cos ( 2 θ ) d θ
For ∫ 1 d θ \int 1 \, d\theta ∫ 1 d θ
∫ 1 d θ = θ \int 1 \, d\theta = \theta ∫ 1 d θ = θ
For ∫ cos ( 2 θ ) d θ \int \cos(2\theta) \, d\theta ∫ cos ( 2 θ ) d θ
∫ cos ( 2 θ ) d θ = sin ( 2 θ ) 2 \int \cos(2\theta) \, d\theta = \frac{\sin(2\theta)}{2} ∫ cos ( 2 θ ) d θ = 2 s i n ( 2 θ )
Combine the results:
50 ∫ ( 1 + cos ( 2 θ ) ) d θ = 50 ( θ + sin ( 2 θ ) 2 ) 50 \int (1 + \cos(2\theta)) \, d\theta = 50 \left(\theta + \frac{\sin(2\theta)}{2}\right) 50 ∫ ( 1 + cos ( 2 θ )) d θ = 50 ( θ + 2 s i n ( 2 θ ) )
Step 4: Back-substitute θ \theta θ
Recall that x + 5 = 10 sin ( θ ) x + 5 = 10 \sin(\theta) x + 5 = 10 sin ( θ )
sin ( θ ) = x + 5 10 , θ = arcsin ( x + 5 10 ) \sin(\theta) = \frac{x + 5}{10}, \quad \theta = \arcsin\left(\frac{x + 5}{10}\right) sin ( θ ) = 10 x + 5 , θ = arcsin ( 10 x + 5 )
Also, use the double-angle formula for sin ( 2 θ ) \sin(2\theta) sin ( 2 θ )
sin ( 2 θ ) = 2 sin ( θ ) cos ( θ ) \sin(2\theta) = 2 \sin(\theta) \cos(\theta) sin ( 2 θ ) = 2 sin ( θ ) cos ( θ )
From the substitution, cos ( θ ) = 1 − sin 2 ( θ ) = 1 − ( x + 5 10 ) 2 \cos(\theta) = \sqrt{1 - \sin^2(\theta)} = \sqrt{1 - \left(\frac{x + 5}{10}\right)^2} cos ( θ ) = 1 − sin 2 ( θ ) = 1 − ( 10 x + 5 ) 2
Substitute back into the result:
50 θ + 25 sin ( 2 θ ) = 50 arcsin ( x + 5 10 ) + 25 ⋅ 2 ⋅ x + 5 10 ⋅ 1 − ( x + 5 10 ) 2 50 \theta + 25 \sin(2\theta) = 50 \arcsin\left(\frac{x + 5}{10}\right) + 25 \cdot 2 \cdot \frac{x + 5}{10} \cdot \sqrt{1 - \left(\frac{x + 5}{10}\right)^2} 50 θ + 25 sin ( 2 θ ) = 50 arcsin ( 10 x + 5 ) + 25 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 10 x + 5 ⋅ 1 − ( 10 x + 5 ) 2
Simplify:
50 arcsin ( x + 5 10 ) + 5 ( x + 5 ) 1 − ( x + 5 10 ) 2 50 \arcsin\left(\frac{x + 5}{10}\right) + 5(x + 5) \sqrt{1 - \left(\frac{x + 5}{10}\right)^2} 50 arcsin ( 10 x + 5 ) + 5 ( x + 5 ) 1 − ( 10 x + 5 ) 2
Final Answer:
∫ 75 − 10 x − x 2 d x = 50 arcsin ( x + 5 10 ) + 5 ( x + 5 ) 1 − ( x + 5 10 ) 2 + C \int \sqrt{75 - 10x - x^2} \, dx = \boxed{50 \arcsin\left(\frac{x + 5}{10}\right) + 5(x + 5) \sqrt{1 - \left(\frac{x + 5}{10}\right)^2} + C} ∫ 75 − 10 x − x 2 d x = 50 arcsin ( 10 x + 5 ) + 5 ( x + 5 ) 1 − ( 10 x + 5 ) 2 + C
Please comment below if you find any error in this solution.
If this solution helps, then please share this with your friends.
Please subscribe to my
Youtube channel for video solutions to similar questions.
Keep Smiling :-)












Leave a comment