









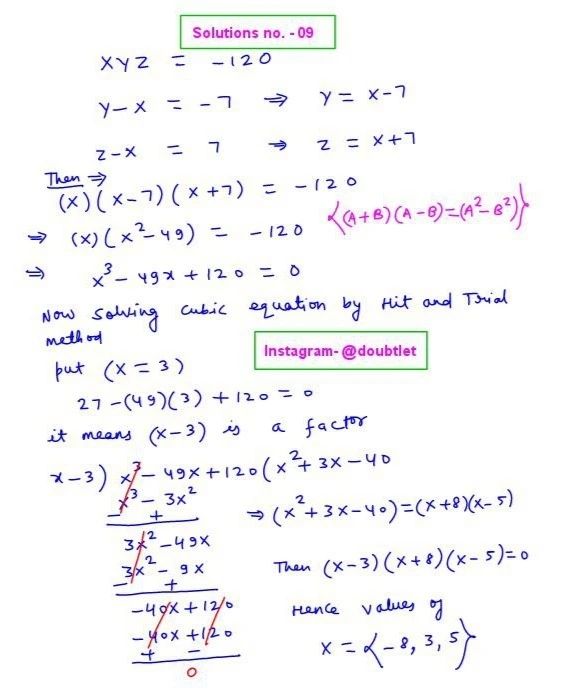
Question :
Find the steady-state vector for the matrix below.
(type an integer or simplified fraction for each matrix element.)

Solution:

Neetesh Kumar | October 18, 2024
Linear Algebra Homework Help
This is the solution to Math2B Course: Linear Algebra
Assignment: Ch5 Section 9 Question Number 4
Contact me if you need help with Homework, Assignments, Tutoring Sessions, or Exams for STEM subjects.
You can see our Testimonials or Vouches from here of the previous works I have done.
Get Linear Algebra Homework Help
Step-by-step solution:
To find the steady-state vector, we need to solve for , which satisfies the equation:
For the given matrix:
This leads to the system of equations:
Step 1: Rearrange the system of equations
Rearranging each equation:
For the first equation:
(Equation 1)
For the second equation:
(Equation 2)
For the third equation:
(Equation 3)
Step 2: Use the condition that
Since the steady-state vector must sum to 1:
(Equation 4)
Step 3: Solve the system of equations
We now have the following system of equations:
Solving this system of equations gives the steady-state vector .
Final Answer
Please comment below if you find any error in this solution.
If this solution helps, then please share this with your friends.
Please subscribe to my Youtube channel for video solutions to similar questions.
Keep Smiling :-)
Comments(0)
Leave a comment